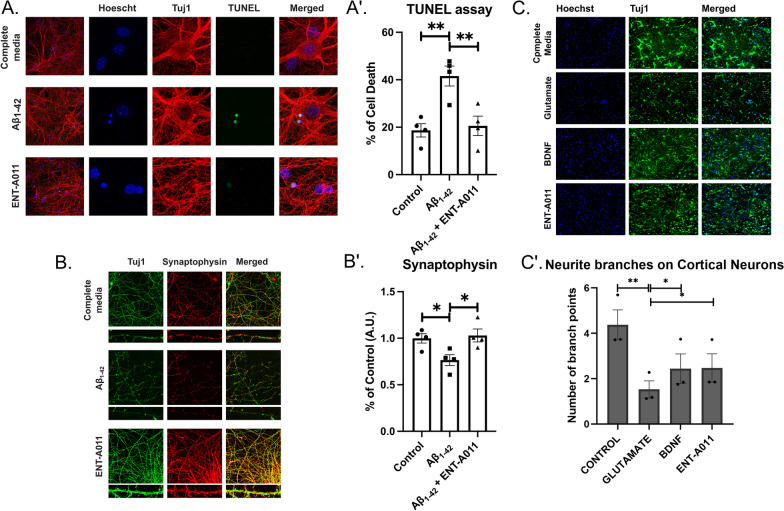
Fig. 5.
ENT-A011 protects mouse hippocampal neurons and rat cortical neurons against Aβ42 and glutamate toxicity respectively. A, A′, ENT-A011 reduces Aβ42 induced hippocampal neuron cell death. Primary hippocampal neurons were treated with Aβ42 for 48 h in presence of ENT-A011 and cell death was quantified using TUNEL assay. Representative images from 4 independent experiments. Data are shown as SEM. One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s Test correction: **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001. B, B′ ENT-A011 protects against Aβ42-induced hippocampal synapse loss. Primary hippocampal neurons were treated with Aβ42 for 4 h in presence of ENT-A011, followed by staining against synaptophysin to assess synapse number. Total Synaptophysin area was normalized to total Tuj1 area in each image. Representative images from 4 independent experiments. Data are shown as SEM. One-way ANOVA, Tukey’s Test correction: ** p < 0.01. ENT-A011 reverts the decrease of neurite branches caused by glutamate on rat Cortical neurons. Representative fluorescence microscopy images of Immunostaining for Tuj1 in cortical neurons treated with BDNF or ENT-A011 for 1 h before glutamate treatment (C). Quantification of neurite branches (C′). N = 3, error bars represent S.E.M., Student’s t-test against Control; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. White Scalebars = 20 μm, Yellow Scalebars = 5 μm