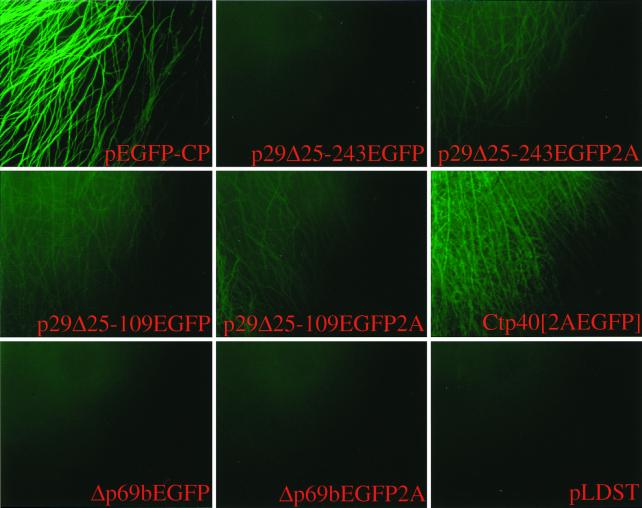
FIG. 3.
Micrographs of EGFP-expressing C. parasitica strains. Agar plugs containing transfected fungal mycelia were transferred from regeneration plates to cellophane-overlaid PDA plates on day 4 posttransfection and placed at the edge of a glass coverslip. The mycelia were allowed to grow between the coverslip and the cellophane for 2 days and then transferred to a glass slide for observation (see Materials and Methods). Mycelia attached to the coverglass were observed under a fluorescent microscope at ×100 magnification. Vector constructs used for transfection are indicated at the bottom of each panel and include p29Δ25-243EGFP, p29Δ25-243EGFP2A, p29Δ25-109EGFP, p29Δ25-109EGFP2A, Ctp40[2AEGFP], Δp69bEGFP, and Δp69bEGFP2A. A colony transfected with synthetic transcripts derived from wild-type virus cDNA, pLDST, served as a negative control, while a transformant in which the EGFP gene (pEGFP-CP) is expressed from the C. parasitica GPD gene promoter (Pgpd) was used as a positive control.