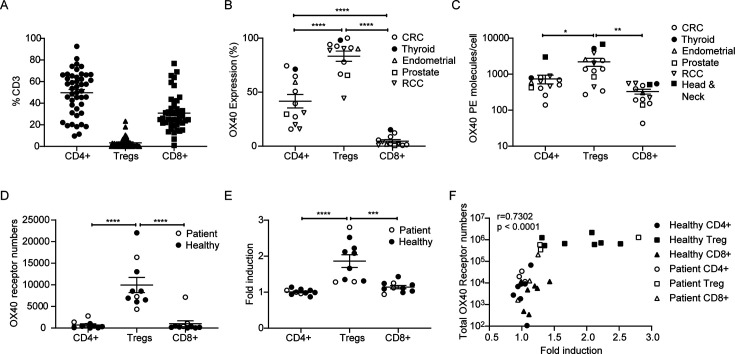
Figure 6.
anti-hOX40 and anti-PD-1 combination increases cytokine production from hPBMC cultures. (A) Resected tumor samples were analyzed for CD4, CD8 and Treg populations n=45 for CD4 and CD8 and n=39 for Treg. (B) hOX40 expression on resected tumor samples on CD4+effectors, Tregs and CD8+T cells, n=12. (C) hOX40 receptor density on resected tumor samples was determined using BD Bioscience Quantibrite beads n=13. (D) Analysis of total OX40 receptor numbers/cell in healthy donor (filled circles) and patient (open circles) PBMCs activated for 2 days with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads n=10. (E) Fold induction of FcγRIII ADCC following healthy (filled circles) and patient (open circles) PBMCs activation for 2 days with anti-CD3/anti-CD28 beads, separation into cell type and then incubated with 10 µg/mL anti-OX40 (GSK3174998), n=10. (F) Correlation of total hOX40 receptor numbers (as determined by numbers of hOX40 receptors per cell × % hOX40+cells) with ADCC fold induction in response to anti-hOX40 treatment of cells isolated from healthy and patient donors activated as in D and E. n=10. ****p<0.0001, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05 mean±SEM B–E–Tukey’s multiple comparison one-way analysis of variance F–Pearson correlation. ADCC, antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity; FcγR, Fc gamma receptors; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; PD-1, programmed cell death protein-1; RCC, renal cell carcinoma; Treg, regulatory T cells.