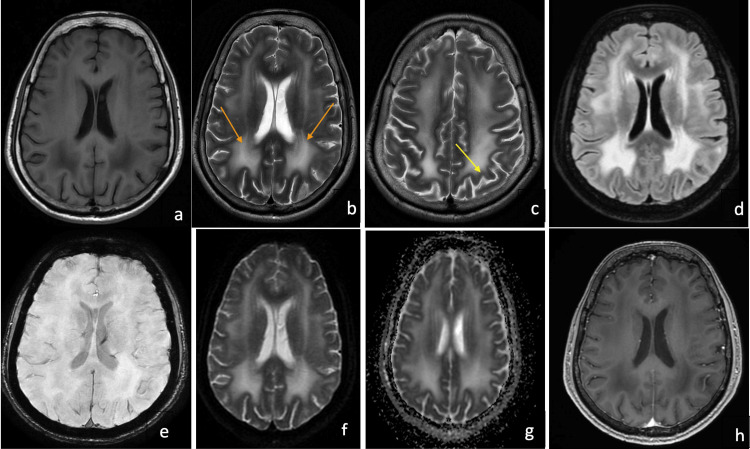
Figure 1. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain in the index case.
1a. T1 weighted axial MRI of the brain showing bilateral symmetrical hypointensity in the periventricular white matter, 1b. T2 weighted axial MRI of the brain showing bilateral symmetrical hyperintensities in the periventricular white matter (orange arrows), 1c. T2 axial MRI brain highlighting the involvement of the subcortical U-fibers (yellow arrow), 1d. FLAIR hyperintensities noted in the bilateral periventricular white matter, 1e. Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) showed no evidence of microbleeds, 1f. and 1g. Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) and attenuation diffusion coefficient (ADC) images demonstrate hyperintense signals in the periventricular white matter suggesting a T2 shine-through effect (probably due to vasogenic edema resulting from hyperpermeability of blood capillaries secondary to LAMA2 protein defect), 1h. T1 contrast images demonstrate the lack of contrast enhancement in the white matter lesions.