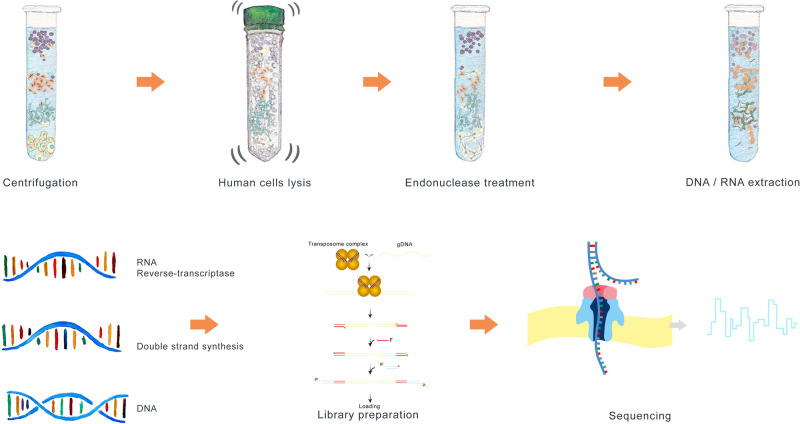
Fig. 1. Metagenomics workflow.
The first step involves spinning the sample. Most of the human cells settle at the bottom, allowing for the collection of supernatant containing mainly microorganisms. The remaining human cells in the supernatant are lysed using mechanical disruption to release the DNA. A nonspecific endonuclease is added to digest the cell-free DNA and RNA present in the supernatant. DNA and RNA-containing microorganisms are extracted. After the extraction, RNA is converted into complementary DNA (cDNA) using the enzyme reverse transcriptase. The single-stranded cDNA is used as a template to synthesise a complementary strand, forming double-stranded DNA. The library preparation is performed using SQK-RPB004—Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT). Elements of this Figure are adapted with permission from ONT.