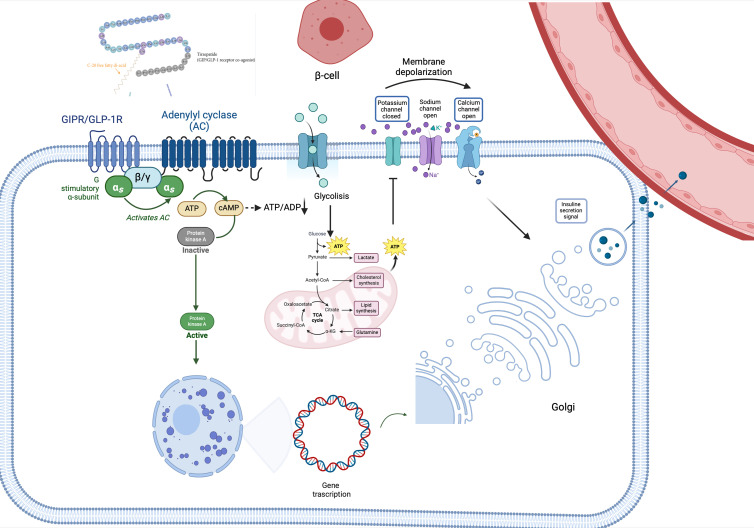
Figure 1.
Tirzepatide’s pathway signaling. TZP binds its receptor, leading to the activation of adenylyl cyclase-cAMP-protein kinase A (PKA) pathway and thus stimulating glucose metabolism (glycolysis and Krebs Cycle). The increase of intracellular ATP levels hesitates in the closure of plasma membrane K+ channels, thus triggering β-cell depolarization. Due to depolarization, voltage-gated Ca2+ channels become open, favoring the entrance of Ca2+ into the cell, which concomitantly stimulates the releasing of calcium from the endoplasmic reticulum. This leads to the release of insulin into the bloodstream. Additionally, PKA stimulates insulin gene transcription, leading to insulin synthesis. αs, in vivo-subunit; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; β/γ, G protein β/gamma subunits; cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; GIP-R/GLP-1R, gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptor/glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor; PKA, adenylyl cyclase-cAMP-protein kinase A.