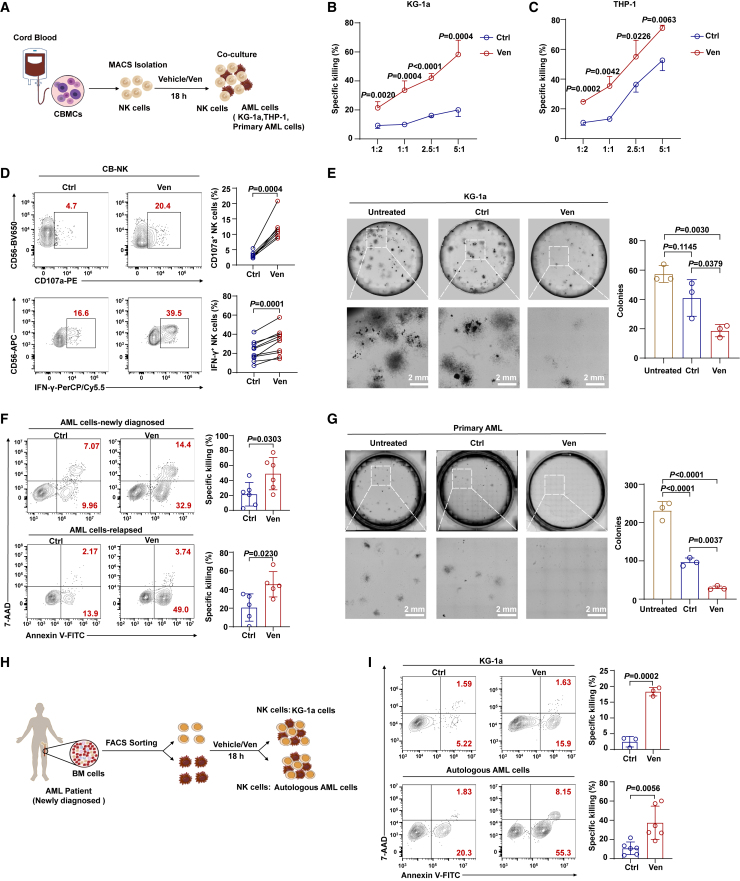
Figure 1.
Venetoclax enhances the cytotoxicity of cord blood and AML patient-derived NK cells against AML in vitro
(A) Schematic representation of the cytotoxicity assays using CB-NK cells.
(B and C) Untreated CB-NK cells or those pretreated with 400 nM venetoclax for 18 h were incubated with KG-1a or THP-1 cells (2 × 104 cells per well) at different effector-to-target ratios for 4 h, followed by Annexin V/7-AAD assay (n = 3/4, biological replicates). The results represent three independent experiments using NK cells from different donors. The calculation of the specific killing is provided in the STAR Methods.
(D) Representative flow cytometry plots (left) and summary data (right) of CD107a (n = 7, biological replicates) and IFN-γ (n = 10, biological replicates) production by CB-NK cells treated with or without 400 nM venetoclax. The results represent three independent experiments.
(E) Colony formation assay using KG-1a cells co-cultured with venetoclax-treated or untreated CB-NK cells at a ratio of 2.5:1 (n = 3, biological replicates). Equal numbers of AML cells (2 × 103 cells per dish) were used in the colony formation assays, and the colonies were counted after 14 days. The results represent three independent experiments using NK cells from three different donors, with detailed experimental procedures in the STAR Methods.
(F) Cytotoxicity assay using venetoclax-treated or untreated CB-NK cells (5 × 104 cells per well) against primary AML cells from newly diagnosed (n = 6, biological replicates) or relapsed patients (n = 5, biological replicates) at a 2.5:1 ratio for 4 h. Primary AML cell viability was assessed using flow cytometry with the Annexin V/7-AAD assay. The results represent three independent experiments using NK cells from different donors.
(G) Colony formation assay using primary AML cells co-cultured with venetoclax-treated or untreated CB-NK cells at a ratio of 2.5:1 (n = 3, biological replicates). Equal numbers of primary AML cells (1 × 104 cells per dish) were used in the colony formation assays, and the colonies were counted after 14 days. The results represent three independent experiments using NK cells and primary AML cells from different donors.
(H) Experimental setup of co-culture assays using NK cells derived from fresh bone marrow (BM) of newly diagnosed patients with AML.
(I) Cytotoxicity assay using NK cells derived from fresh AML BM samples (5 × 104 cells per well) treated with or without 400 nM venetoclax against KG-1a cells (n = 3, biological replicates) or autologous AML cells (n = 6, biological replicates) at a 2.5:1 ratio for 4 h. The results for autologous AML cells are representative of four independent experiments using NK cells from six different donors.
Data were analyzed using two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test (B, C, F, and I), paired Student’s t test (D), or one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (E and G). Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD).
See also Figures S1 and S2.