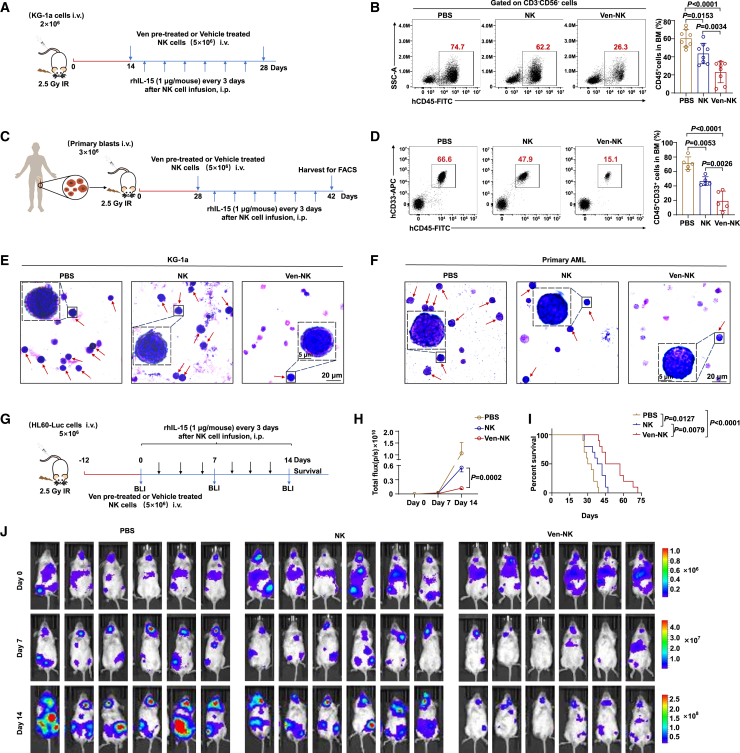
Figure 2.
Venetoclax potentiates NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity against AML in vivo
(A) Schematic illustration of KG-1a mouse model construction (3 groups, n = 8/group).
(B) Representative flow cytometry plots (left) and quantification (right) illustrating BM engraftment of KG-1a cells. Two weeks post-injection of KG-1a cells, engraftment of KG-1a cells (human CD45+, gating from human CD3−CD56−) in the BM was determined by flow cytometry. NK cells used for in vivo studies were generated following the procedures described in the STAR Methods. The results were obtained from three independent experiments using NK cells from eight donors.
(C) Schematic outline of AML patient-derived xenograft model generation (3 groups, n = 5/group).
(D) Representative flow cytometry plots (left) and quantification illustrating BM engraftment of primary AML cells (right). Four weeks post-AML injection, the engraftment of primary AML cells (human CD45+ CD33+) in the BM was assessed through flow cytometry. NK cells used for in vivo studies were generated following the procedures described in the STAR Methods. The results were obtained from three independent experiments.
(E and F) Representative images of Wright-Giemsa BM smear staining of KG-1a (left) and primary AML cell (right) xenograft mice. Red arrowheads indicate leukemia cells.
(G) Schematic outline of HL60-Luc mouse model construction (3 groups, n = 10/group), with detailed experimental procedures in the STAR Methods. AML burden was monitored by bioluminescence imaging at the indicated time points.
(H) Kinetic analysis of AML burden in each group assessed by bioluminescence imaging. Statistical analysis was performed for the average radiance between venetoclax-pretreated and non-pretreated NK cell groups 14 days post-NK cell infusion.
(I) Kaplan-Meier survival analysis of HL60-Luc-engrafted mice.
(J) Imaging of AML burden using bioluminescence.
Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test (B and D), unpaired Student’s t test (H), or log rank Mantel-Cox test (I). For (B) and (D), the data are presented as mean ± SD. For (H), data are presented as mean ± SEM.