Fig. 1.
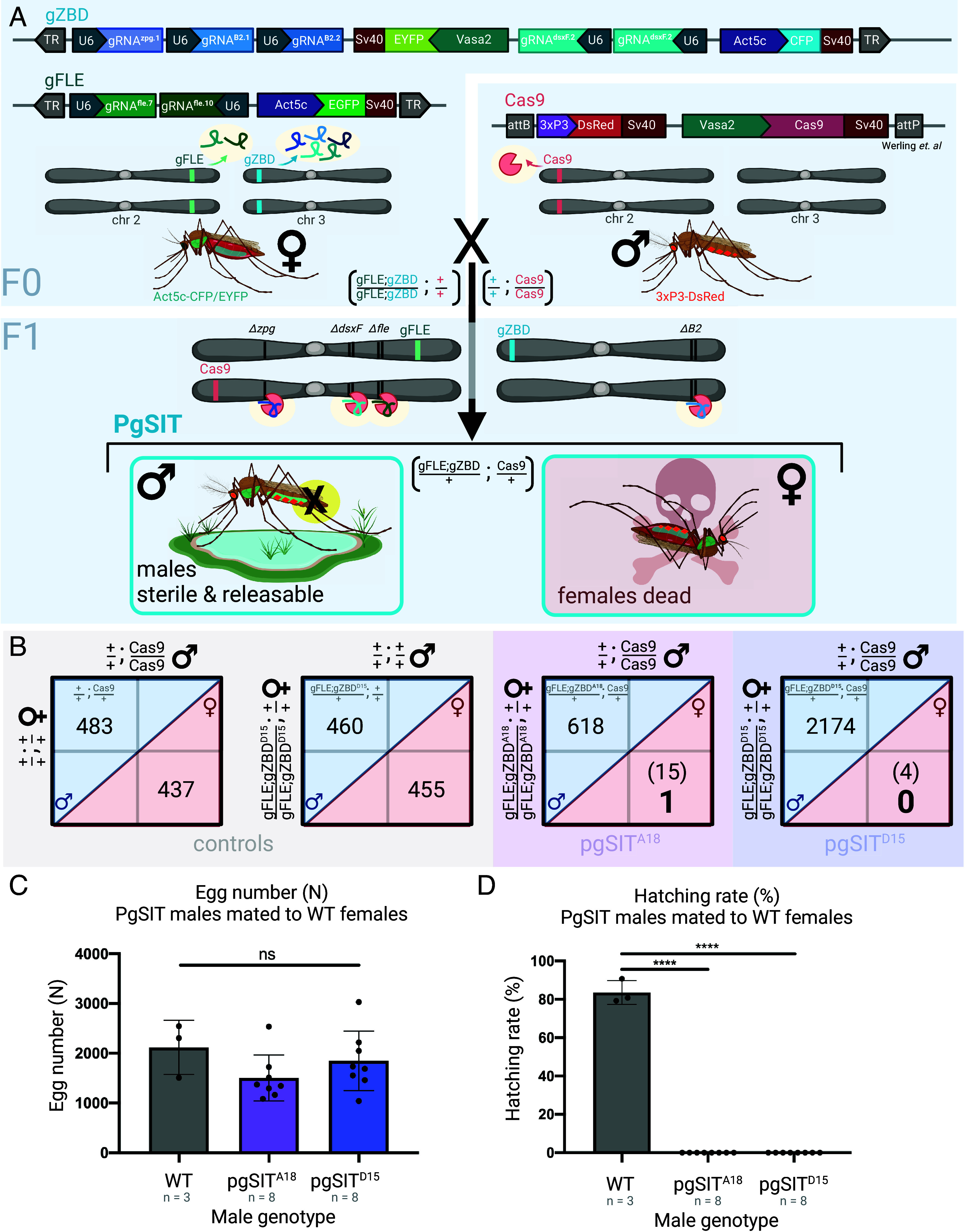
Homozygous pgSIT gRNA females crossed to Cas9 males produce nearly exclusively sterile male F1 offspring. (A) gZBD transgenics express one gRNA targeting zero population growth (zpg) (lavender), two gRNAs targeting β2-tubulin (periwinkle), and two gRNAs targeting the female-specific exon 5 of doublesex (dsxF) (teal) under the expression of individual PolIII U6 promoters, some carrying modified scaffolds (Methods). Also included is a whole-body fluorescent selectable marker, Actin5c-m2turquoise (denoted CFP for brevity), as well as a Vasa2-EYFP marker to aid in germline visualization, a marker which was not visible in these lines. gZBD transgenic lines were individually crossed to a second line, gFLE, to generate double homozygous transgenic lines termed (gFLE;gZBD). gFLE targets femaleless (fle) via two gRNAs also under the expression of the Pol III U6 promoter, and includes an Actin5c-EGFP cassette for selection by whole-body fluorescence. A third line, Cas9, expresses Cas9 in the germline under the Vasa2 promoter and includes a 3xP3-DsRed cassette for selection by central nervous system fluorescence. Crossing (gFLE;gZBD) females to Cas9 males yields transheterozygous pgSIT individuals who bear all three transgenes, resulting in active mosaic mutagenesis, and causing female killing and male sterilization. (B) Among control and pgSIT test crosses, the female-killing phenotype was quantified in the F1 generation, reported as male and female sibling pupa counts. Male and female counts are delineated within blue and red diagonal areas, respectively. Control crosses of Cas9 or (gFLE;gZBDD15) homozygotes to wild type result in approximately equal F1 male and female pupa counts. Crosses between (gFLE;gZBDA18) or (gFLE;gZBDD15) homozygous females and Cas9 homozygous males result in significantly reduced F1 female pupa numbers (in parentheses) (P < 0.0001 for both groups, Binomial test). The number of pupae which survived to adulthood to fly are denoted in large bold font. (C) Crossing 50 pgSIT males to 50 wild type females results in statistically the same number of eggs being laid. Three cage replicates and eight cage replicates shown for wild type control and pgSIT test genotypes respectively. Raw egg counts shown (ns, one-way ANOVA, Dunnett's multiple comparisons test). Mean and SD shown. (D) Crossing 50 pgSIT males to 50 wild type females results in complete sterilization of females when assayed by hatching rate (n% = n 1-d-old larvae/n eggs laid), with high significance compared to the wild type control group (P < 0.0001 for each group, one-way ANOVA, Dunnett's multiple comparisons test). Three cage replicates and eight cage replicates shown for wild type control and pgSIT test genotypes respectively. Created with Biorender.com.
