Figure 4.
RAS pathway-mutated CMML cells rely on MCL1 overexpression to maintain their survival at BP
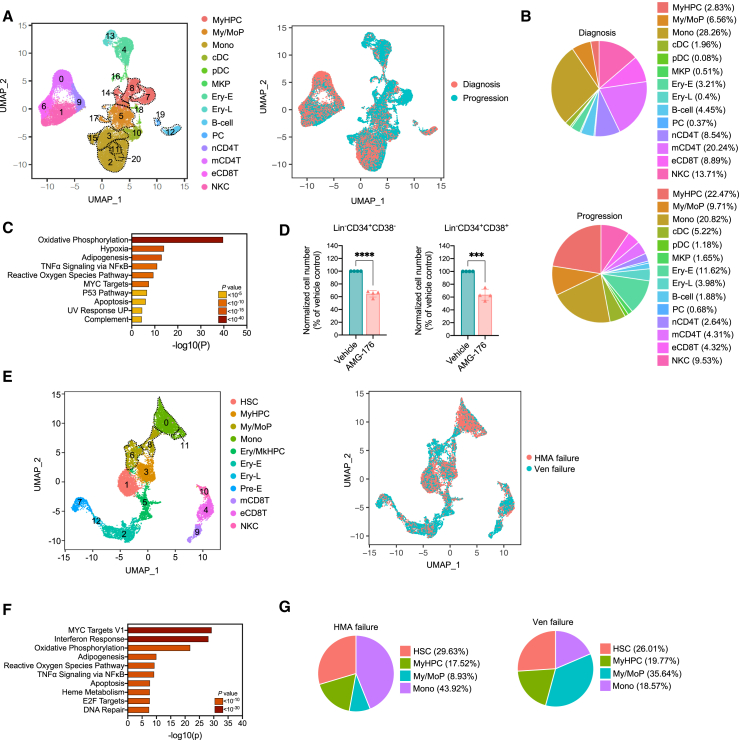
(A) UMAP of scRNA-seq data for pooled single MNCs isolated from BM samples of six RAS pathway mutant CMML patients at diagnosis (n = 16,372) and at BP after HMA therapy failure (n = 19,541). Each dot represents one cell. Different colors represent the cluster cell-type identity (left) or sample of origin (right). MyHPC, myeloid hematopoietic progenitor cells; My/MoP, myelo/monocytic progenitors; Mono, monocytes; cDC, classical dendritic cells; pDC, plasmacytoid dendritic cells; MKP, megakaryocyte precursors; Ery-E, early erythroid precursors; Ery-L, late erythroid precursors; B cell, B lymphocytes; PC, plasma cells; nCD4T, naive CD4+ T cells; mCD4T, memory CD4+ T cells; eCD8T, effector CD8+ T cells; NKC, natural killer cells. Dashed lines indicate single clusters in each cell-type population.
(B) Distribution of MNC populations at diagnosis (top) and progression (bottom) among the clusters shown in (A).
(C) Pathway enrichment analysis of the genes that were significantly upregulated in the monocytic populations (clusters 2, 3, 11, 15, and 20) shown in (A) at the time of BP after HMA therapy failure compared with those at diagnosis (adjusted p ≤ 0.05). The top 10 hallmark gene sets are shown.
(D) Numbers of live Lin–CD34+CD38– HSCs and Lin–CD34+CD38+ MyHPCs from CMML patients with BP after treatment with vehicle or AMG-176 (n = 4, 20 nM) for 48 h. Lines represent means ± SD. Statistical significance was calculated using a two-tailed Student’s t test (∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001).
(E) UMAP of scRNA-seq data for pooled single MNCs isolated from BM samples obtained from a representative CMML patient at the time of BP after HMA therapy failure (n = 6,209) and subsequent failure to venetoclax-based therapy (n = 6,795). Each dot represents one cell. Different colors represent the cluster cell-type identity (left) or the sample of origin (right). HSC, hematopoietic stem cells; MyHPC, myeloid hematopoietic progenitor cells; My/MoP, myelo/monocytic progenitors; Mono, monocytes; Ery/MkHPC, erythroid/megakaryocytic hematopoietic progenitor cells; Ery-E, early erythroid precursors; Ery-L, late erythroid precursors; Pre-E, pre-erythrocytes; mCD8T, memory CD8+ T cells; eCD8T, effector CD8+ T cells; NKC, natural killer cells.
(F) Pathway enrichment analysis of the genes that were significantly upregulated in MyHPCs at the time of venetoclax failure compared with those at the time of BP after HMA therapy failure (adjusted p ≤ 0.05). The top 10 hallmark gene sets are shown.
(G) Distribution of myeloid cell types among the myeloid compartments at BP after HMA therapy failure (left) and venetoclax-based therapy failure (right).