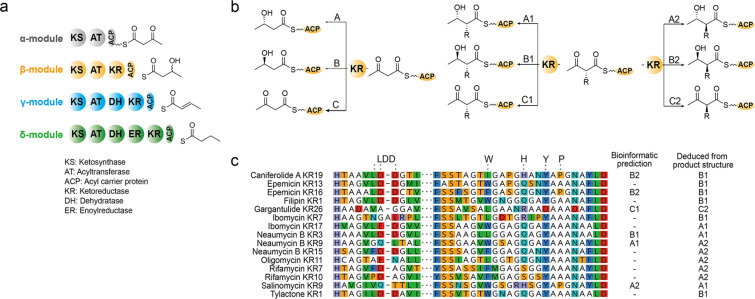
Figure 1.
(a) Domain compositions and the products of α-, β-, γ- and δ-modules in cis-AT PKSs. (b) Stereocontrol of KR domains. KRs can be classified into A-type (β-ʟ-hydroxy), B-type (β-ᴅ-hydroxy), and C-type (reduction-incompetent; β-keto) depending on the product structure and into subtypes 1 (non-epimerizing, α-ᴅ-substitution product) and 2 (epimerizing, α-ʟ-substitution product). (c) Sequence alignment of KR domains whose stereoselectivity cannot be predicted based on the reported motifs. The labels show the product name and the order of the module where KR is located in the PKS assembly line (starting from the module with condensation function). KR types predicted based on the fingerprint motifs and deduced from product structure identified by chemical methods are shown on the right.