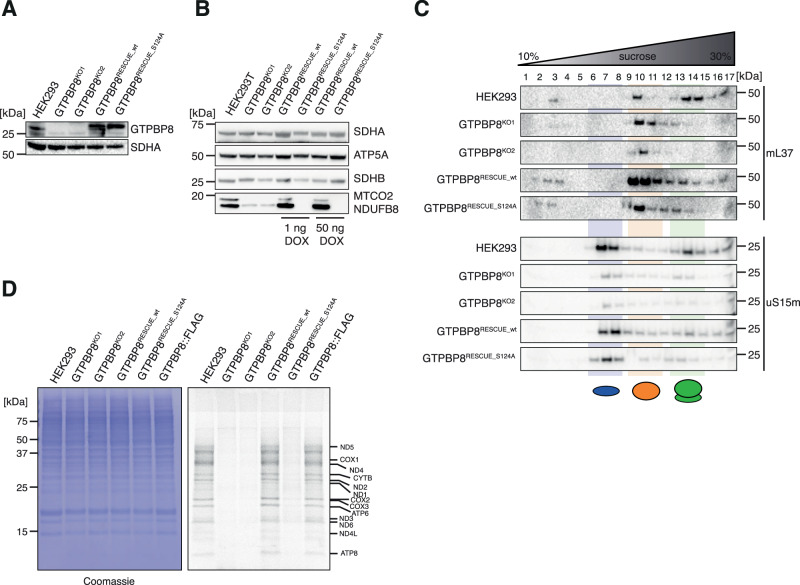
Fig. 5. GTP hydrolysis is important for GTPBP8 function.
A Western blotting analysis of control HEK293, GTPBP8KO1, GTPBP8KO2, GTPBP8RESCUE_wt and GTPBP8RESCUE_S124A samples to confirm GTPBP8 knock-out compared to the rescue cell lines. Anti-GTPBP8 antibody was used to compare GTPBP8 endogenous expression with the overexpression in rescue cell lines. SDHA was used as a loading control (n = 1 independent experiments). B Western blotting analysis to test OxPhos steady-state levels in GTPBP8KO1 and GTPBP8KO2 compared to wild-type HEK293 and rescue cell lines GTPBP8RESCUE_wt and GTPBP8RESCUE_S124A. Overexpression was induced prior to the experiment using 1 ng/ml and 50 ng/ml of doxycycline. Whole-cell lysates were resolved via SDS-PAGE. Membranes were probed using the OxPhos antibody cocktail against nuclear-encoded proteins of complexes V (ATP5A) and I (NDUFB8) and mtDNA-encoded complex IV protein MTCO2. SDHA and SDHB were used as loading controls (n = 1). C Sucrose gradient centrifugation analysis to assess mitoribosome sedimentation patterns in GTPBP8KO1 and GTPBP8KO2 compared to HEK293, GTPBP8RESCUE_wt and GTPBP8RESCUE_S124A. Mitochondrial lysates were loaded onto 10-30 % isokinetic sucrose gradients and obtained fractions were analyzed via western blotting. Membranes were probed for mt-LSU MRP, mL37, and mt-SSU MRP, uS15m (n = 3 independent experiments). D In vivo translation assay of GTPBP8KO1 and GTPBP8KO2 cell lines compared to HEK293, GTPBP8RESCUE_wt and GTPBP8RESCUE_S124A. Cells were labeled with a [35S]-methionine and cysteine mix upon cytosolic translation inhibition. Whole cell lysates were resolved by SDS-PAGE and the signal was later detected via autoradiography. The loading was determined using Coomassie staining (n = 1 independent experiment). Source data are provided as a Source Data file.