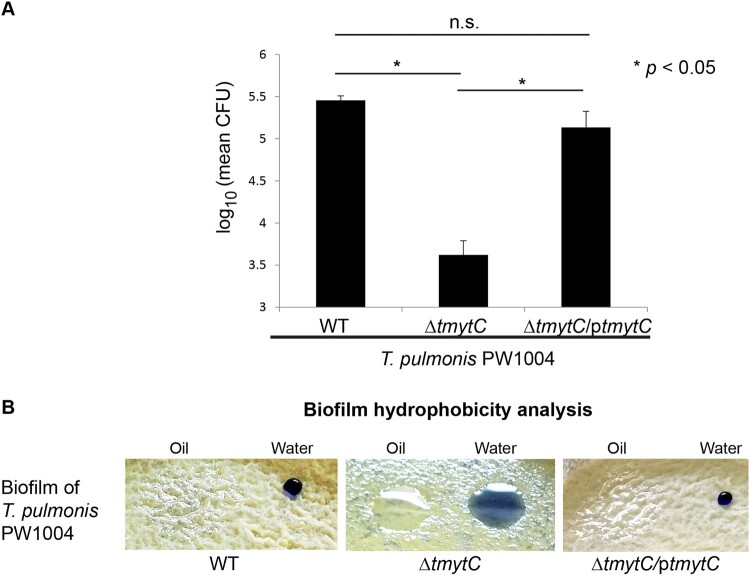
Figure 5.
Altered adherence to contact lens, biofilm hydrophobicity, and PHMB susceptibility of the tmytC knockout mutant. (a) Adherence of the wild-type and tymtC mutants to contact lenses in vitro as analysed by CFU counting analysis. The number of bacteria recovered from the contact lenses inoculated with PW1004ΔtmytC was significantly lower compared to those inoculated with the PW1004-WT (P < 0.05) and the PW1004ΔtmytC/ptmytC (P < 0.05) mutants. Error bars indicated means ± SEM of three independent experiments. (b) The PW1004ΔtmytC surface was more hydrophilic compared to the PW1004-WT. Droplets of oil or water containing trypan blue were applied to the surface of the biofilm lawn. In the PW1004-WT and tymtC complemented mutant, the oil spread into a thin film over the surface, suggesting that the cell surface was hydrophobic in nature. In contrast, the water droplet continued to spread (i.e. more hydrophilic) and the oil droplet spread less (i.e. less hydrophobic) in the tymtC knockout mutant.