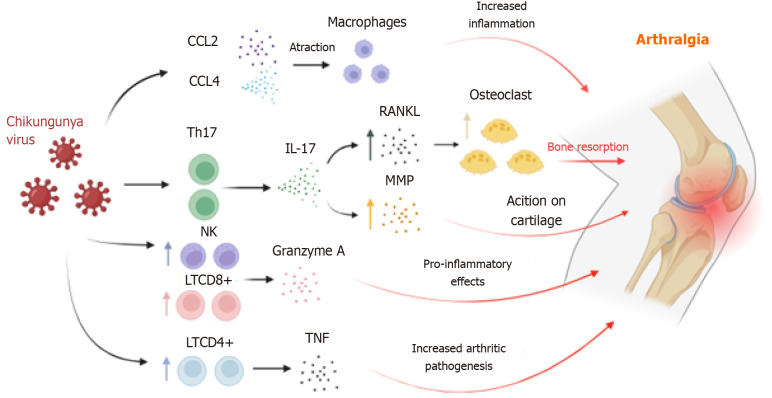
Figure 1.
Supposed mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of arthritis caused by Chikungunya virus. The elevation in levels of pro-inflammatory chemokines induces T helper type 17 response polarization, leading to interleukin-17 expression and subsequent increase in receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand. Granzyme A released by natural killer cells and CD8+ T cells targets type IV collagen, contributing to progressive joint damage. Th17: T helper type 17; CCL4: C-C motif ligand 4; NK: Natural killer; LTCD8: CD8 T lymphocytes; LTCD4: CD4 T lymphocytes; RANKL: Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa-Β ligand; MMP: Matrix metalloproteinases; IL: Interleukin; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.