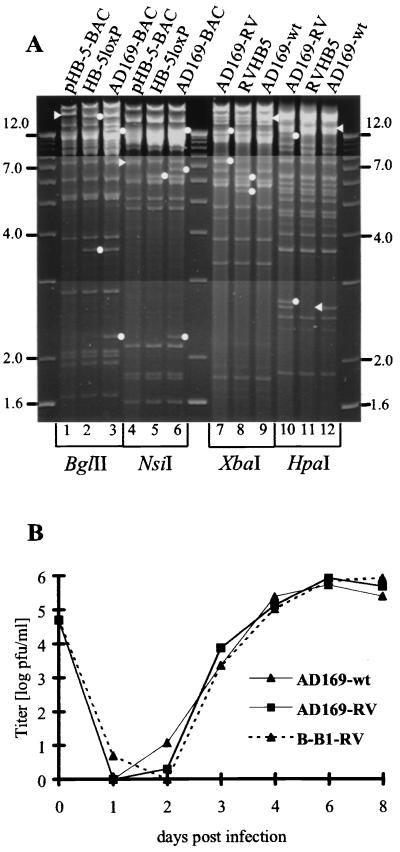
FIG. 2.
Recombinase Cre-mediated excision of the BAC vector sequences results in a nearly wt AD169-RV. (A) Lanes 1 to 6, restriction enzyme digests of HCMV BAC plasmids pHB-5, HB-5loxP, and AD169-BAC isolated from bacteria; lanes 7 to 12, digestion of viral DNA extracted from cells infected with viruses reconstituted from BAC plasmids AD169-BAC (AD169-RV) and pHB-5 (RVHB5), or the parental strain AD169-wt. Relevant restriction sites are depicted in Fig. 1. Arrowheads, restriction endonuclease fragments; dots, additional fragments resulting from manipulations described in the legend for Fig. 1. (B) Single-step growth curve of recombinant viruses. AD169-RV is compared to parental HCMV strain AD169-wt and B-B1-RV, an AD169-BAC-based mutant virus with the Tn sequences stably integrated at the 3′-terminal end of UL78, nt 114124. MRC-5 cells were infected at an MOI of 0.1. Virus titers from cells and supernatant were determined in duplicate by a standard plaque assay at the indicated time points.