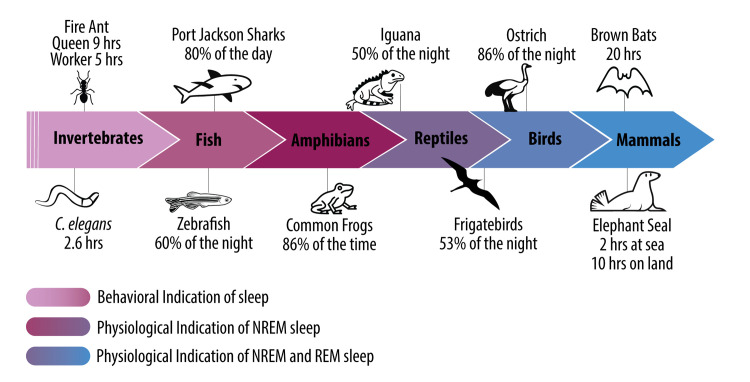
Fig 5. Sleep variability across species.
Sleep duration varies markedly across the entire animal kingdom, from invertebrates to mammals. In most invertebrates and fish, sleep is defined behaviorally (e.g., for fire ants [276] and Port Jackson sharks [277]). Physiological evidence of NREM sleep can be found in a few amphibian species (e.g., the common frog [278]), as well as in reptiles [279]. In birds and mammals, evidence of sleep includes physiological recordings of both REM and NREM sleep, often measured in the lab [280–282]. NREM, nonrapid eye movement; REM, rapid eye movement.