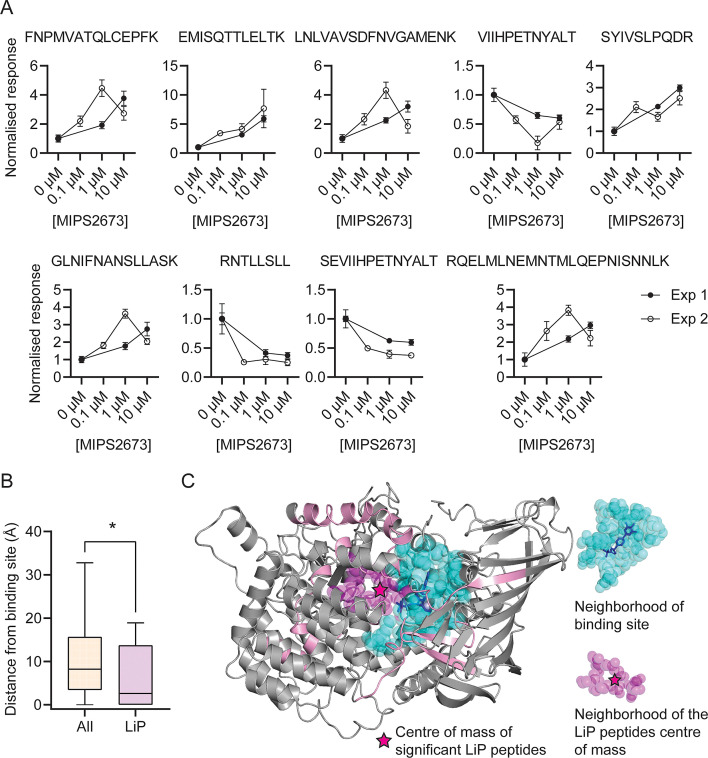
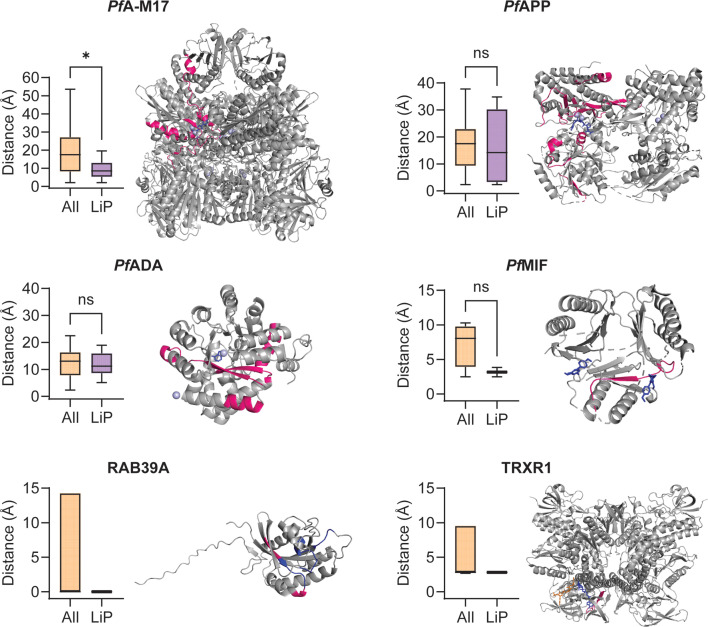
Figure 5. Features of structurally significant PfA-M1 limited proteolysis coupled with mass spectrometry (LiP-MS) peptides.
(A) Relative abundance of the significant LiP peptides commonly identified across two LiP-MS experiments following P. falciparum proteome lysate treatment with MIPS2673. The mean ± SEM of at least three independent lysate incubations per condition and experiment are shown. (B) Median distances between atoms of the nine significant LiP peptides or all detected PfA-M1 peptides and the PfA-M1 binding cleft residues. *p<0.05, Mann-Whitney test. (C) MIPS2673 binding site on PfA-M1 determined by X-ray crystallography (PDB: 8SLO), and approximation of the MIPS2673 binding site using the significant PfA-M1 LiP peptides and centre of mass calculation. The significant LiP peptides are mapped onto the PfA-M1 structure with MIPS2673 bound and are shown in pink. The drug ligand is shown in blue and the centre of mass of the significant LiP peptides is shown by a magenta star. The area in cyan represents the neighbourhood of the drug binding site determined as residues within 6.44 Å of bound MIPS2673. The neighbourhood of the LiP peptide centre of mass (residues within 6.44 Å of the centre of mass) is depicted in magenta.
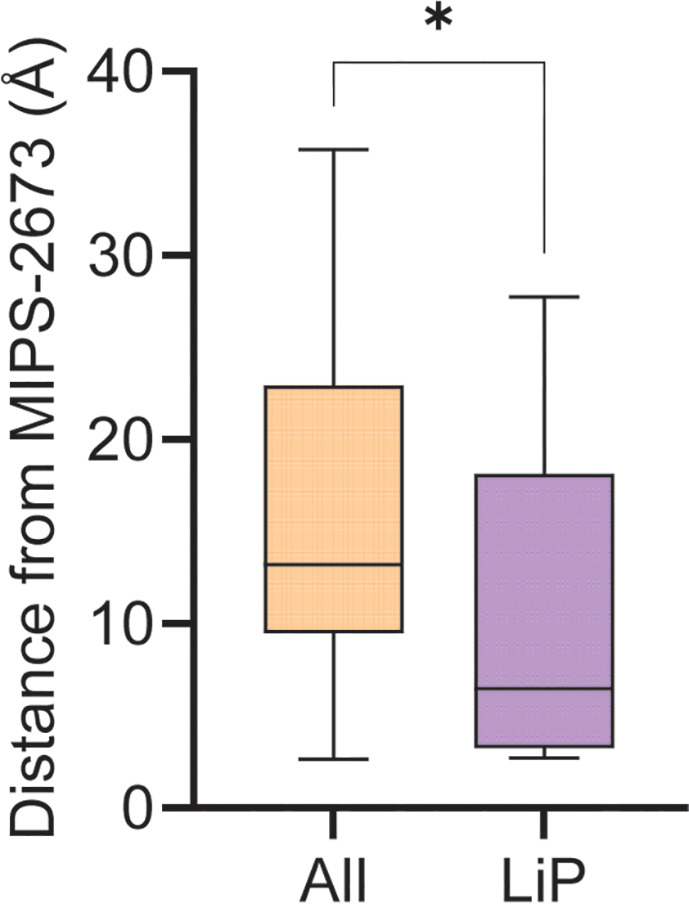
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Minimum distance of significant limited proteolysis coupled with mass spectrometry (LiP-MS) or all other PfA-M1 peptides from bound MIPS2673.