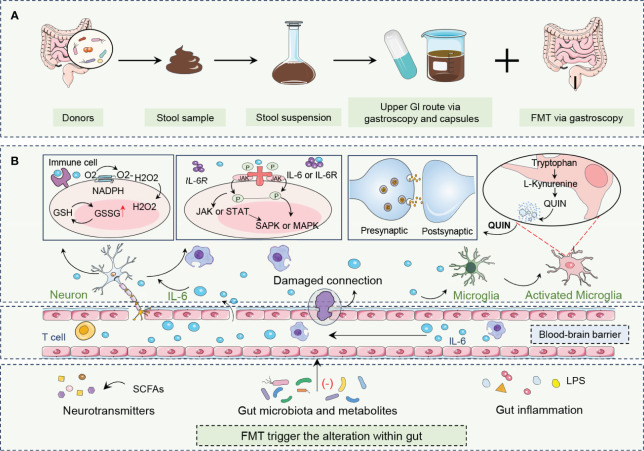
Figure 2.
FMT procedure and its roles in combating depression. (A) FMT is an innovative treatment that encompasses the acquisition, processing, and administration of fecal material from healthy donors to patients with depression. (B) By altering neurotransmitters, gut microbiota and metabolites, and gut inflammation, FMT rebalances gut biota enhances microbe-gut-brain axis communication, restores neurotransmitter homeostasis, and reduces neuroinflammation. FMT modulation of the immune system, particularly through the alteration of IL-6 levels, is crucial to alleviating depressive symptoms. FMT can influence the central nervous system by altering gut microbiota composition and activating beneficial signaling pathways, including those mediated by the vagus nerve, which is a major neural link between the gut and the brain. Fecal microbiota transplantation, FMT; Gastrointestinal, GI; Glutathione, GSH; Oxidized glutathione, GSSG; Hydrogen peroxide, H2O2; Interleukin 6, IL-6; Interleukin 6 receptor, IL-6R; Janus kinase, JAK; Lipopolysaccharide, LPS; Mitogen-activated protein kinase, MAPK; Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen, NADPH; Oxygen, O2; Quinolinic acid,QUIN; Stress-activated protein kinase, SAPK; Short-chain fatty acids, SCFAs; Signal transducer and activator of transcription, STAT.