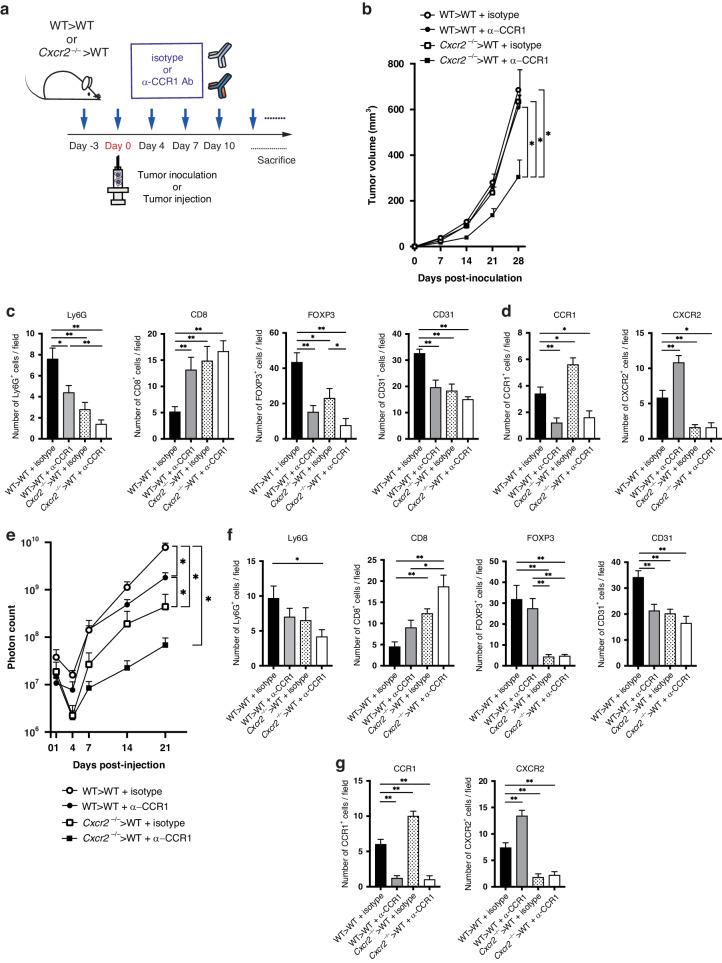
Fig. 7. Effect of anti-CCR1 mAb, KM5908, on tumor growth and liver metastasis in the context of genetic CXCR2 knockout.
a Experimental scheme of KM5908 or isotype control administration in WT > WT mice and Cxcr2−/− > WT mice. b Tumor growth curves of transplanted MC38 tumors in the four treatment groups: isotype-treated WT > WT mice, KM5908-treated WT > WT mice, isotype-treated Cxcr2−/− > WT mice and KM5908-treated Cxcr2−/− > WT mice. Bars, mean ± SEM (Student’s t test; *P < 0.05). n = 4–5 mice for each group. c Immunohistological staining for Ly6G+ neutrophils, CD8+ T cells, FOXP3+ Treg cells and CD31+ endothelial cells around transplanted MC38 tumors. Scale bar, 100 mm. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 by Student’s t test. d Immunohistological staining for CCR1+ and CXCR2+ cells. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 by Student’s t test. e Quantification of liver metastatic lesions (photon counts) in the four treatment groups: isotype-treated WT > WT mice, KM5908-treated WT > WT mice, isotype-treated Cxcr2−/− > WT mice and KM5908-treated Cxcr2−/− > WT mice. Bars, mean ± SEM (Mann–Whitney U test; *P < 0.05). n = 3–6 mice for each group. f Immunohistological staining for Ly6G+ neutrophils, CD8+ T cells, FOXP3+ Treg cells and CD31+ endothelial cells around transplanted MC38 tumors. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 by Student’s t test. g Immunohistological staining for CCR1+ and CXCR2+ cells. **P < 0.01 by Student’s t test.