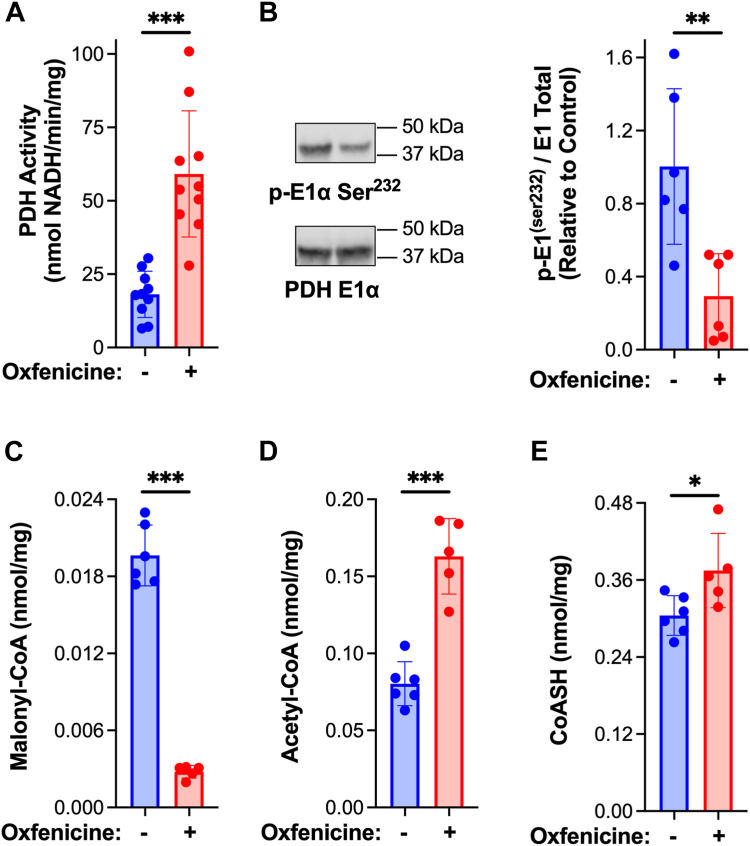
Figure 2.
Inhibition of β-oxidation activates pyruvate dehydrogenase and increases CoASH and acetyl-CoA content in the heart. Male C57BL/6N mice received an intraperitoneal injection of saline or oxfenicine (0.15 mg/g) at 12 PM. Hearts were excised 30 min post-injection, homogenized, and mitochondria were isolated (+DCA and NaF). A, PDH activity was measured spectrophotometrically. B, E1α subunit content and phosphorylation status of Ser232 on the PDH E1α subunit were measured by Western blot followed by densitometric analysis. Cardiac tissue excised and frozen 30 min post-oxfenicine injection was extracted, metabolites resolved by reverse phase HPLC and (C) malonyl-CoA, (D) acetyl-CoA, and (E) CoASH quantified by UV/Vis spectroscopy. Values are presented as the mean ± SD (n = 5–9) where significant differences (2-tailed t test) are indicated by ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Each data point indicates a separate animal.