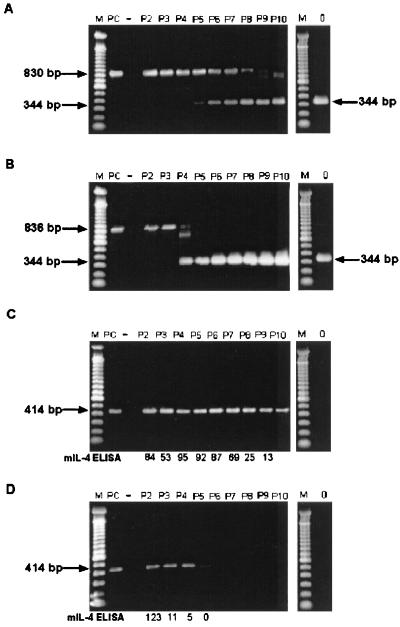
FIG. 4.
RT-PCR analysis of mIL-4 insert stability following passage of chimeric viruses in HeLa cells. Amplimers were obtained and analyzed on 1.5% agarose gels following RT-PCR of viral RNA isolated from sequentially passaged CVB3-PL2-mIL4/46 (A and C) and CVB3/0-mIL4/47 (B and D). ELISA detection of mIL-4 protein is also shown for comparison (C and D). Viruses were passaged 10 times in HeLa cells as described in the text. Amplification of the region containing the insert in the viral RNA populations was accomplished with the primers ID9 and ID10 (A and B); the intact mIL-4 insert was detected as an 836-bp (or 830-bp) product and as a 344-bp product when the insert was deleted. Specific detection of the mIL-4-containing insert was accomplished using primers KNIL4S and KNIL4AS (C and D); the presence intact insert was detected as a 414-bp product, whereas deletion of the product resulted in no amplimer produced. mIL-4 ELISA (C and D), concentration of mIL-4 protein as detected by ELISA for each pass (5 × 105 HeLa cells infected at an MOI of ≥10 with designated viral passage stock, harvested at 6 h p.i.). Specific activities of mIL-4 ranged between 0.13 and 0.61 U/pg. Lanes P2 to P10, results from passages 2 to 10, respectively; lane M, 100-bp ladder (Life Technologies); lane PC, positive control amplification using pCVB3-PL2-mIL4/46 DNA; lane −, negative control (no DNA added) amplification; lane 0, PCR of CVB3/0 virus stock. Gel was stained with Cyber Green (FMC, Philadelphia, Pa.); images were captured using a Nucleo Vision gel documentation system (Nucleo Tech Corp.).