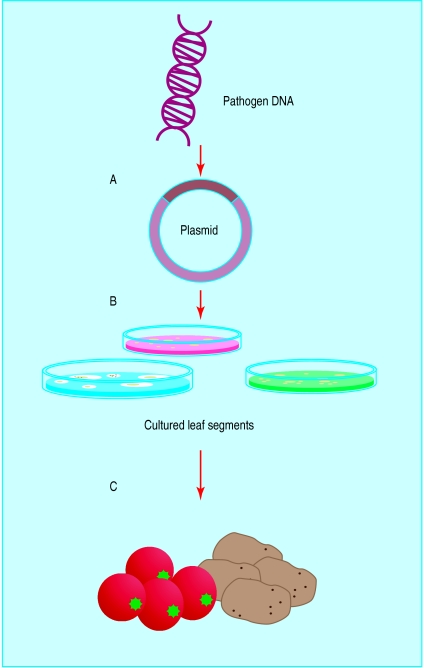
Figure 2.
Principle of delivering vaccines in edible plants. A gene from a human pathogen is inserted into a bacterium that infects plants (A). The bacterium then infects cultured leaf segments of the selected food plant (B), which sprout into whole plants containing the human pathogen gene (C). Once the plant is eaten, it triggers an immune response to the pathogen