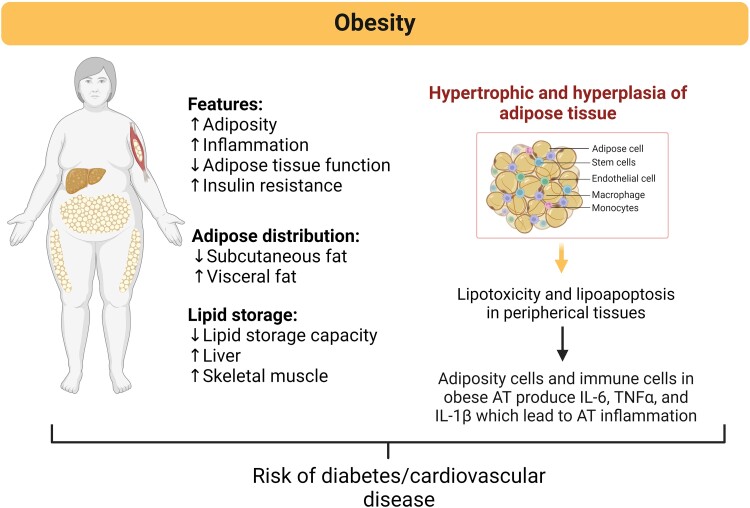
Figure 1.
Adipose tissue features and distribution, and associated damage mechanisms underlying the pathophysiology of obesity. Adipose tissue undergoes several changes in its composition, distribution, and function that increase the risk of developing diabetes, cardiovascular complications, and other metabolic diseases. Unhealthy expansion of adipose tissue during obesity is mainly mediated by hyperplasia and hypertrophy of adipocytes, increasing adipose tissue inflammation driven by activation of proinflammatory adipokines and cytokines, such as IL-6 and TNF-alpha. Created with BioRender.com.