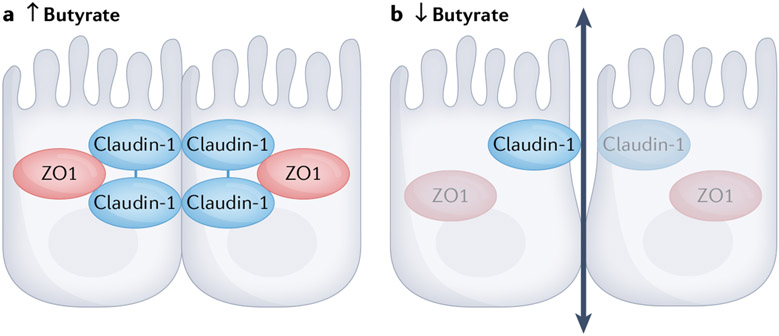
Fig. 2 ∣. The role of butyrate in regulating intestinal epithelial cell tight junctions.
Butyrate regulates the expression of genes encoding tight junction proteins, including claudin-1 and zonula occludens 1 (ZO1), and regulates the distribution of occludins. In the presence of high levels of butyrate, the expression of tight junction proteins and distribution of occludins is such that tight junctions are well formed. In an environment where butyrate levels are low, decreased expression of key proteins that form tight junctions causes the junctions to loosen and increases absorption.