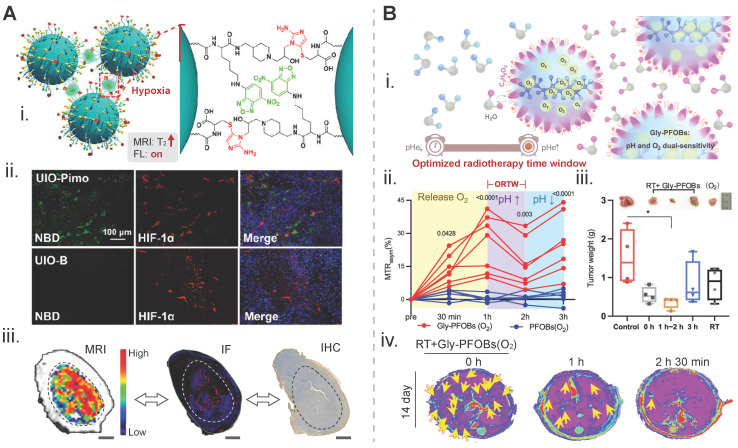
Figure 4.
Biomarker-driven imaging probes for radiotherapy planning. A) Hypoxia-triggered self-assembly of an iron-oxide-based MRI/FL dual-mode nanoprobe, termed as UIO-Pimo, for delineation of the targeted tumor area: (i) design principles for imaging signal amplification; (ii) fluorescent images of tumor tissue slices. Red signal from HIF-1α indicates the hypoxia degree and the green signal from NBD represents the fluorescence of the activatable UIO-Pimo nanoprobe and a non-activatable UIO-B nanoprobe; (iii) the distribution of hypoxic areas within a tumor displayed via the nanoprobe-participated MRI difference value method. IF from HIF-1α, and IHC from commercial hypoxia indicator pimonidazole. Adapted with permission 121. Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society. B) A pH/oxygen-activatable 19F/1H dual-mode nanoprobe for determining an optimal radiotherapeutic window: (i) scheme for the design of the nanoprobe; (ii) dynamic CEST signal changes in a NCI-H460 lung tumor area after injection of Gly-PFOB(O2) or PFOB(O2); (iii) tumor weights of each group on day 14 post-treatment. The time on the x axis indicats the duration of radiation treatment after injection of Gly-PFOB (O2); (iv) T2WI MRI images of the liver in each treatment group, i.e., Gly-PFOB(O2) + RT, Gly-PFOB(O2) + RT at 1 h post injection of nanoprobe, and Gly-PFOB(O2) + RT at 2 h 30 min post injection on day 14 post-treatment. Yellow arrows indicate liver metastasis. Adapted with permission 32. Copyright 2023. Springer Nature. CC BY 4.0 (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/). MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; FL: fluorescence; HIF-1α: hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha; IF: immunofluorescence; IHC: immunohistochemistry.