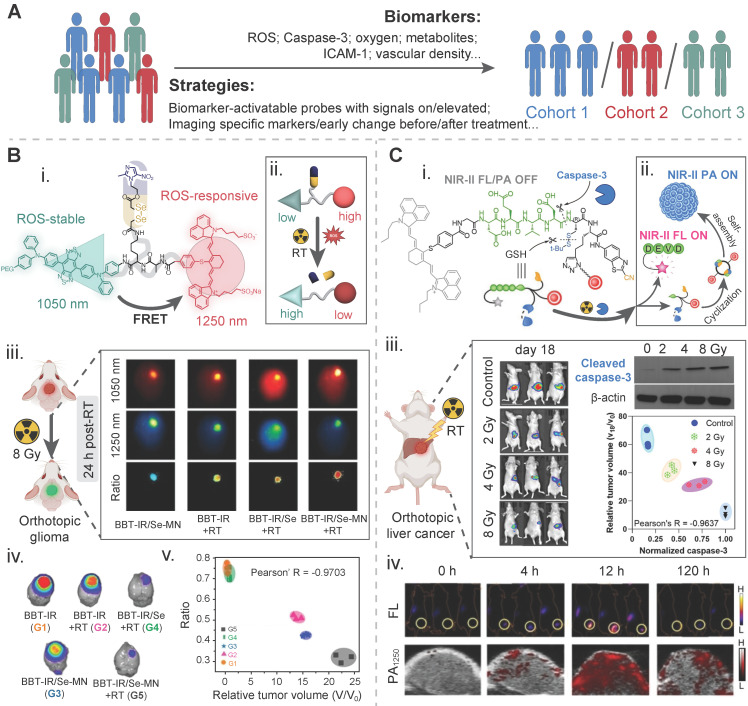
Figure 5.
Biomarker-driven imaging probes for patient stratification. A) Illustration of strategies and biomarkers for radiotherapy stratification. B) A tumor reactive oxygen species (ROS)-activatable ratiometric fluorescent probe for reporting the ROS level during radiosensitizer-enhanced radiotherapy: (i) chemical structure and (ii) activatable mechanism of this nanoprobe; (iii) NIR-II FL images of orthotopic glioma-bearing mice in different treatment groups at 24 h post radiotherapy; (iv) bioluminescence images of the brain in the tumor model in different treatment groups on day 16 post radiotherapy. The intensity is an indicator of the tumor mass; (v) correlation between the ratiometric intensity and the relative tumor volume of these above groups on day 15 post radiotherapy. Adapted with permission 136. Copyright 2023 WILEY-VCH GmbH. C) A caspase-3-activatable organic-inorganic hybrid nanoprobe for reporting the caspase-3 level during radiosensitizer-enhanced radiotherapy: (i) chemical structure and (ii) activatable mechanism of this nanoprobe. The red dot for a nanogapped gold nanoparticle; (iii) bioluminescence images of an orthotopic liver cancer model for measuring the tumor mass via the fluorescence intensity, western blotting images of activated caspase-3 in the tumor tissue, and the correlation between the caspase-3 level and the tumor mass in four treatment groups, i.e., the control (0 Gy), 2 Gy, 4 Gy, and 8 Gy; (iv) fluorescence images and photoacoustic images of ectopic xenograft HepG2 tumors under 8 Gy radiation at different time points after injection of the nanoprobe. Adapted with permission 134. Copyright 2022 WILEY-VCH GmbH.