Figure 6.
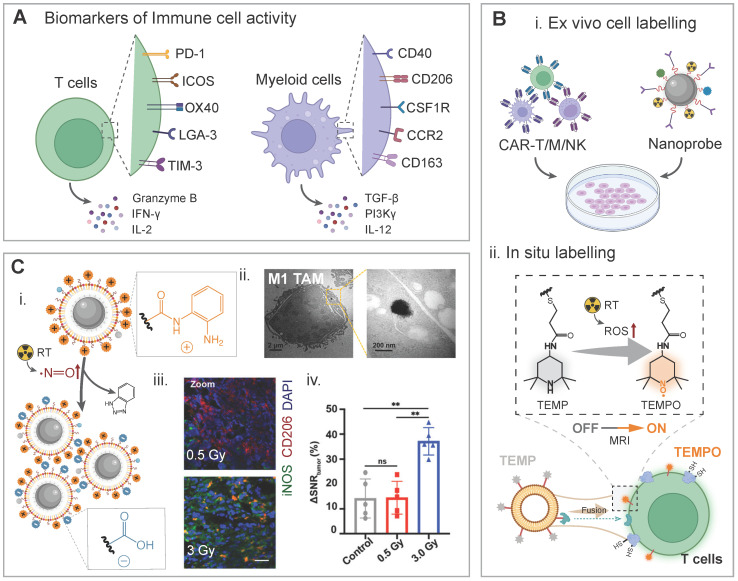
Biomarker-driven imaging probes for immune cells and their activities. A) Schematic illustration of biomarkers for immune cell activities during radiotherapy, including up/down-regulated surface receptors and secreted cytokines. B) Imaging of immune cells can be realized by ex vivo cell labelling and in situ labelling. Imaging-visible nanoprobes were ex vivo labelled with CAR-T/M/NK cells for real-time monitoring of their biodistribution, and T cell-directed liposomes were fused with T cell for in-situ labelling and they were activated when encountering radiation-induced ROS. C) Nitric oxide-triggered self-assembly of the USPIO@OMG nanoprobe for evaluating macrophage polarization during radiotherapy: (i) chemical principle for aggregation of the nanoprobe; (ii) TEM images to confirm the aggregation status of the nanoprobe in M1 macrophages; (iii) CLSM images of tumor slices from two radiation dose-treated groups, red CD206 signal indicates M2 macrophages while the green iNOS signal represents M1 macrophages; (iv) The T2 MRI signal changes in different groups. Adapted with permission 147. Copyright 2023 American Chemical Society.