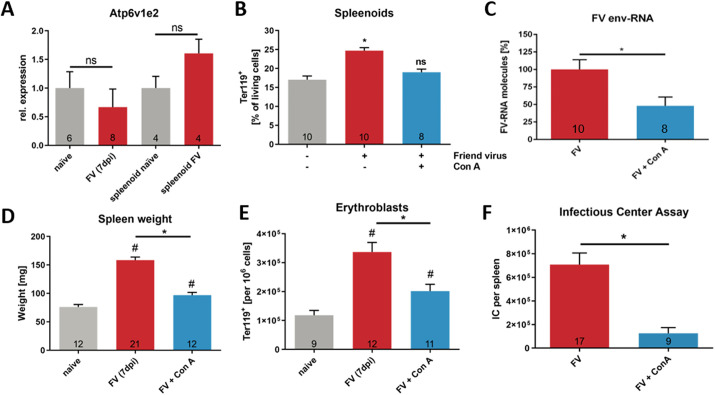
Fig. 6.
Disturbed V-ATPase function leads to reduced virulence of FV. (A) To determine whether V-ATPase expression is altered during FV infection, expression analyses of the subunit Atp6v1e2 of naïve and FV infected Hif-1afl mice (7 dpi) and spleenoids (4 dpi) were performed. (B,C) Spleenoids were treated with FV either alone or in combination with 1 µM ConA. (B) At 4 dpi, the number of erythroblasts (Ter119+) was determined by flow cytometry. (C) Viral load was determined by real time-PCR analyses for FV env expression. Expression was normalized to β-actin expression. (D) Spleen weight of Hif-1afl mice with and without ConA treatment (12 ng/g body weight) was analyzed 7 days after FV infection. (E) The numbers of erythroblasts (Ter119+) in spleens of Hif-1afl mice with or without ConA treatment was determined by flow cytometry. (F) Viral load of Hif-1afl mice with or without ConA treatment was analyzed at 7 dpi. Results are mean±s.e.m. The number of animals tested/experiments is indicated in the graphs. *P<0.05; #P<0.05 compared to naïve mice; ns, not statistically significant (one-way ANOVA and Tukey's multiple comparison test).