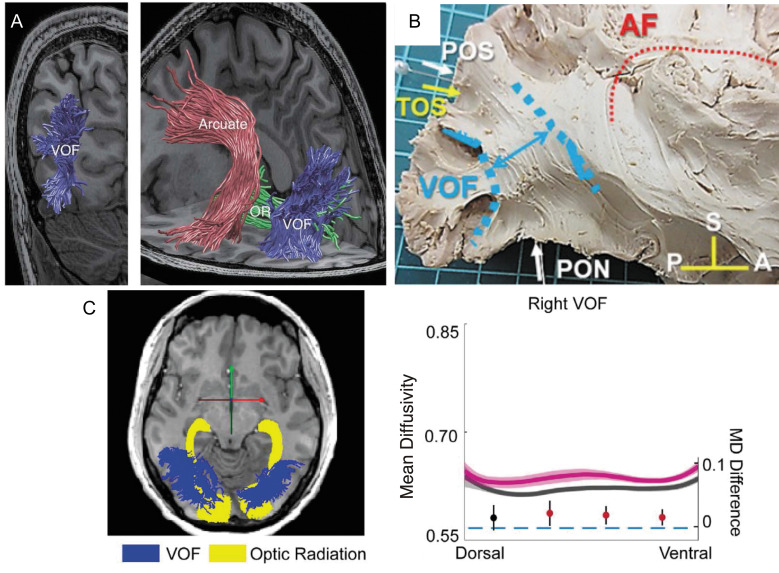
Fig. 6.
Vertical occipital fasciculus. A: The VOF (blue) is identified by tractography, which is overlaid on a T1-weighted image (left image, coronal view; right image, and sagittal view).207 The VOF is lateral to the OR (green) while posterior to the arcuate fasciculus (red). Reprinted with permission from reference 207. B: The VOF identified by Klingler’s dissection (highlighted by blue), which is displayed together with other anatomical landmarks.211 Reprinted by permission from reference 211 (under the Attribution 4.0 International Creative Commons license (CC BY 4.0)). C: Tractometry on the VOF on amblyopia patients.168 Left panel: tractography on the OR (yellow) and VOF (blue) overlaid on a sagittal slice of a T1-weighted image. Right panel: tractometry on the right VOF. The amblyopia group (magenta curve) exhibited higher mean diffusivity (vertical axis, unit: µm2/s) compared with control (dark gray curve). The horizontal axis represents the normalized position along the VOF (left: dorsal, right: ventral). The shadowed area indicates ±1 s.e.m. from the mean in each group. The filled circles showed differences in mean diffusivity (MD) between amblyopia and the control group (the unit is shown on the right side of the plot). The error bar indicates the 95% confidence interval of the differences. Statistically significant differences were marked in red. Reprinted by permission from reference 168. A, anterior; AF, arcuate fasciculus; OR, optical radiation; P, posterior; PON, pre-occipital notch; POS, parieto-occipital sulcus; S, superior; TOS, transverse occipital sulcus; VOF, vertical occipital fasciculus.