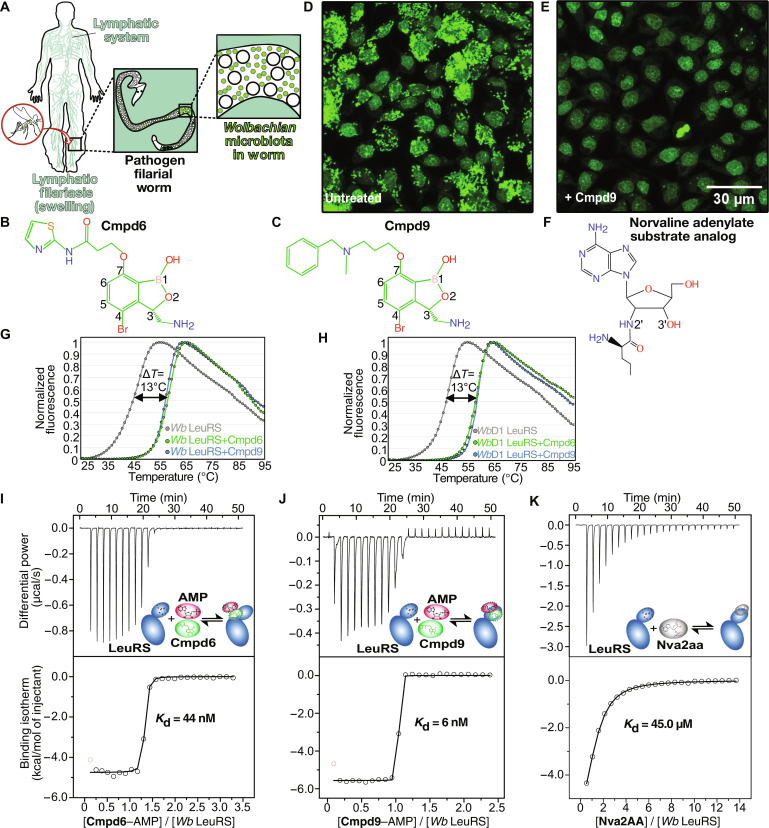
Fig. 1. Benzoxaborole compounds target microbiota Wolbachian LeuRS.
(A) Transmitted by mosquito bites, filarial worm pathogens can reach the lymphatic nodes where they cause severe chronic pain and swelling of tissues. (B, C, and F) Chemical structures of Cmpd6, Cmpd9, and editing substrate analog of norvaline (Nva), respectively. (D) C6/36 insect cells (A. albopictus) stably infected with W. pipientis (wAlbB) were analyzed by fluorescence and high-content image analysis. Single-cell image analysis shows the nucleus (fluorescent large shapes) in the center surrounded by colonizing Wolbachia (small fluorescent dots) in the cytoplasm. (E) Reduction of Wolbachia load in host cells treated with Cmpd9 at 9 μM for 7 days. (G and H) Thermal-shift assays showing the stabilization of Wolbachia LeuRS proteins in the presence of the inhibitors Cmpd6 and Cmpd9. The experiments were performed in triplicates for both the wild-type Wolbachia LeuRS and the construct Wolbachia LeuRS D1 in the presence of AMP. (I, to K) ITC binding experiments showed one order of magnitude higher affinity of Cmpd6/9 in the presence of AMP compared to norvaline posttransfer analog (physiological editing substrate of LeuRS). DSF and ITC experiments were performed in biological and technical triplicates; N = 3.