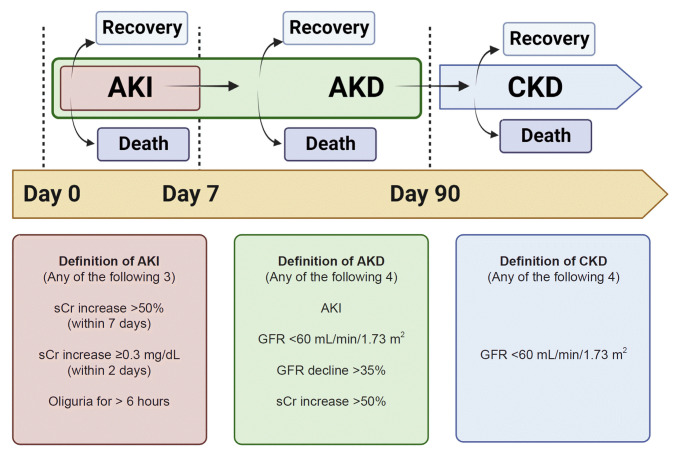
Figure 1. The definition and time frame of AKI, AKD, and CKD.
AKI refers to a rapid and abrupt decline in renal function occurring within a period of 2 to 7 days. In contrast, AKD is characterized by the simultaneous presence of kidney damage and abnormal renal function persisting over an extended 90-day timeframe. It’s important to note that AKI is encompassed within the broader category of AKD, although AKD can also be defined independently without identification of prior AKI. CKD is defined by persistent kidney function or structural abnormalities lasting for at least 3 months (or 90 days). Markers of structural kidney injury such as albuminuria or hematuria can also be used to define AKD and CKD. Outcomes, such as mortality or the recovery of renal function, may develop across AKI, AKD, and CKD.
AKD, acute kidney disease; AKI, acute kidney injury; CKD, chronic kidney disease; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; sCr, serum creatinine.