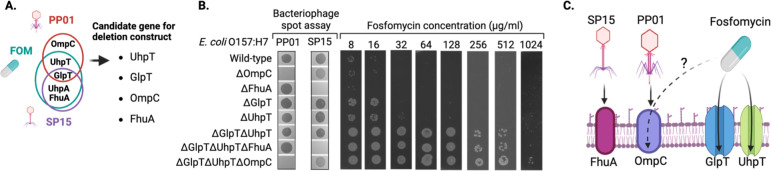
Fig 5.
Identification of a prevalent mutation in antibiotic-resistant bacteria following fosfomycin treatment, phage treatment alone, or combined phage and fosfomycin therapy. (A) Detection of five commonly mutated genes in the context of phage and antibiotic treatment. Given the dependence of uhpT promoter activity on uhpA, a deletion mutant was constructed for four genes (uhpT, glpT, ompC, and fhuA). (B) Alterations in the sensitivity to the phage and changes in the MIC values of fosfomycin observed in the deletion mutant. (C) Schematic illustration depicting the phage receptor and fosfomycin uptake channel, as observed in this study.