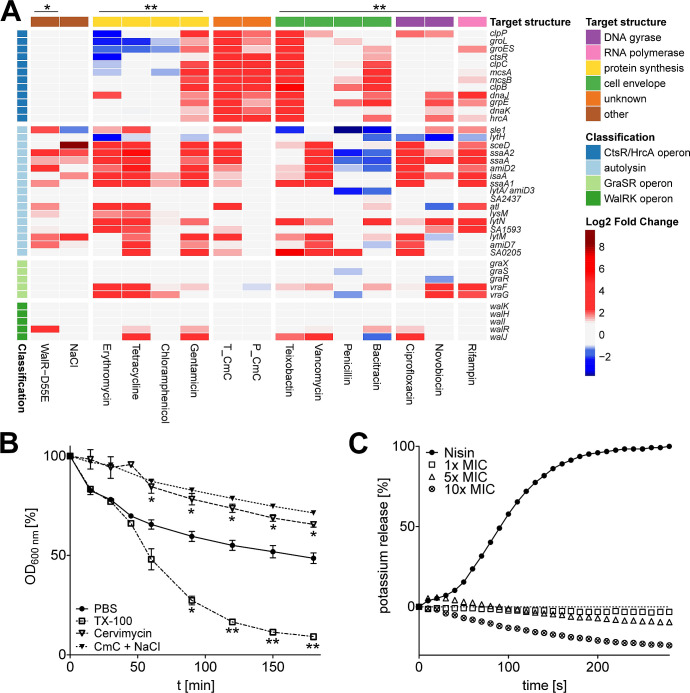
Fig 6.
Cervimycin causes a unique induction of the heat shock stress response and autolysin expression, without subsequent cell lysis. Cervimycin induced the expression of the CtsR/HrcA operon and of most autolysins (A), a response also seen for other antibiotic classes (comparison with data from Delauné et al. [42] [*] and Jones et al. [40] [**]). Upregulation (log2 FC ≥ 1, red color) and downregulation (log2 FC ≤ −1, blue color) on the transcriptomic level are compared. T_CmC, cervimycin transcriptome; P_CmC, cervimycin proteome. (B) Triton X-100 (TX-100) leads to cell lysis in S. aureus, significantly reducing the optical density, while cervimycin treatment prevented cell lysis in the absence and presence of sodium chloride; P: *, ≤0.0423, **, ≤0.0059. (C) The release of potassium ions by the pore former nisin, but not by cervimycin, confirmed the lack of membrane activity. The graph shows the typical result of one of three experiments.