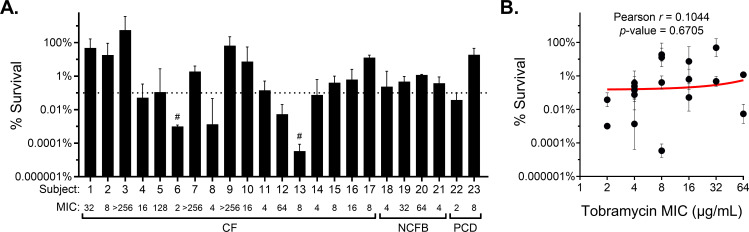
Fig 1.
Ex vivo tobramycin efficacy is highly variable and independent of antibiotic resistance. (A) Percent survival of P. aeruginosa in fresh spontaneous expectorated sputum from individuals with CF, NCFB, or PCD after ex vivo treatment with 300 µg/mL tobramycin for 24 h. Data are presented as the percent of CFUs recovered on Pseudomonas isolation agar (PIA) post tobramycin treatment compared to vehicle (PBS) control. Values are reported as mean ± SD of ≥2 aliquots of each sputum sample tested. # indicates no CFUs recovered after tobramycin treatment (limit of detection, 4 × 101 CFU/mL). A horizonal dashed line indicates 99.9% reduction. The tobramycin MIC (µg/mL) for each untreated P. aeruginosa population is indicated. (B) Linear regression and Pearson correlation of P. aeruginosa population survival in ex vivo treated sputum versus population MIC, excluding hyperresistant populations (MIC ≥ 80).