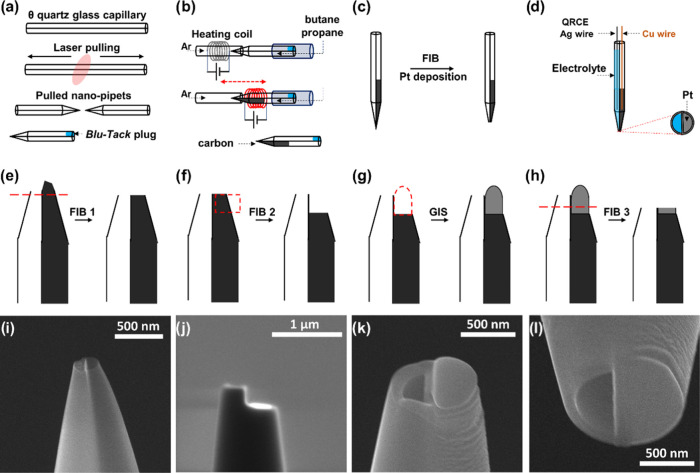
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the fabrication steps of the dual-probe tip. After laser-pulling of the double-barrel capillary, one barrel is closed using Blu-Tack (a), and a butane-propane mixture is passed through the open barrel. To deposit carbon pyrolytically, the tip of the pipet is heated in a two-step process under an argon atmosphere (b). After pyrolysis, the probe is assessed with FIB-SEM and a GIS (c). Schematic of the fabricated dual-probe (d): one working electrode of deposited Pt on pyrolytic carbon in the barrel of the probe connected with a Cu wire, the open barrel is filled with electrolyte, and an Ag-wire QRCE is inserted from the back. The currents and applied voltages of each working electrode with respect to ground are controlled separately. The pipet is assessed with FIB-SEM in the first step (e), then milled to prepare a platform for Pt deposition on the carbon side (f). Pt deposition using GIS (g). FIB cutting after GIS (h). Corresponding SEM micrograph (side view) of the dual probe before (i) and after (j) FIB cutting. SEM micrograph of the end of a dual-probe (k) showing deposited Pt (right) and open barrel (left). Micrograph of the tip after Pt deposition and FIB milling (l).