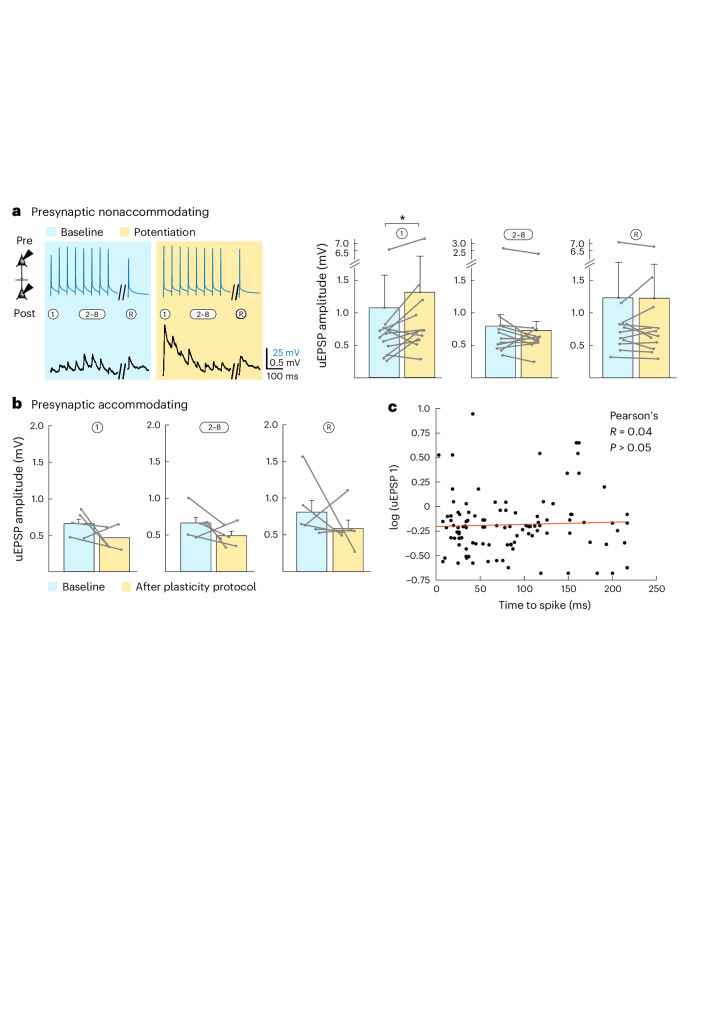
Fig. 4. In vitro synaptic plasticity between LA neurons.
a, In vitro-induced potentiation between connections that involve presynaptic nonaccommodating neurons before (blue) and after (yellow) the Hebbian association protocol. Left: Example trace of averaged AP-evoked (top) uEPSPs (bottom) for one connection taken 5 min before and 10 min after the induction protocol. Right: Average normalized amplitudes of 1, 2–8 and R uEPSPs excluding failures. Data were analyzed by two-tailed paired Wilcoxon signed-rank test (uEPSP 1: W = 10, *P = 0.042; uEPSP 2–8: W = 20, P = 0.303; uEPSP R: W = 32, P = 1; all with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons; n = 11 connections). Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. b, Average normalized amplitudes of 1, 2–8 and R uEPSPs, excluding failures. Unlike connections with a presynaptic nonaccommodating neuron, connections with a presynaptic accommodating neuron did not potentiate. Data were analyzed by two-tailed, paired Wilcoxon signed-rank test (uEPSP 1: W = –13, P = 0.2188; uEPSP 2–8: W = –14, P = 0.1875; uEPSP R: W = –19, P = 0.0625; all Bonferroni corrected, n = 6 connections). Data are shown as mean ± s.e.m. c, Synaptic strength could not be predicted by presynaptic time to spike, as this did not correlate with uEPSP 1 amplitude before the induction of plasticity. This suggests that before fear conditioning, neurons that are prime candidates to be recruited into the fear memory trace do not have stronger local connectivity. Recordings were made in 14- to 19-day-old Wistar rats of both sexes.