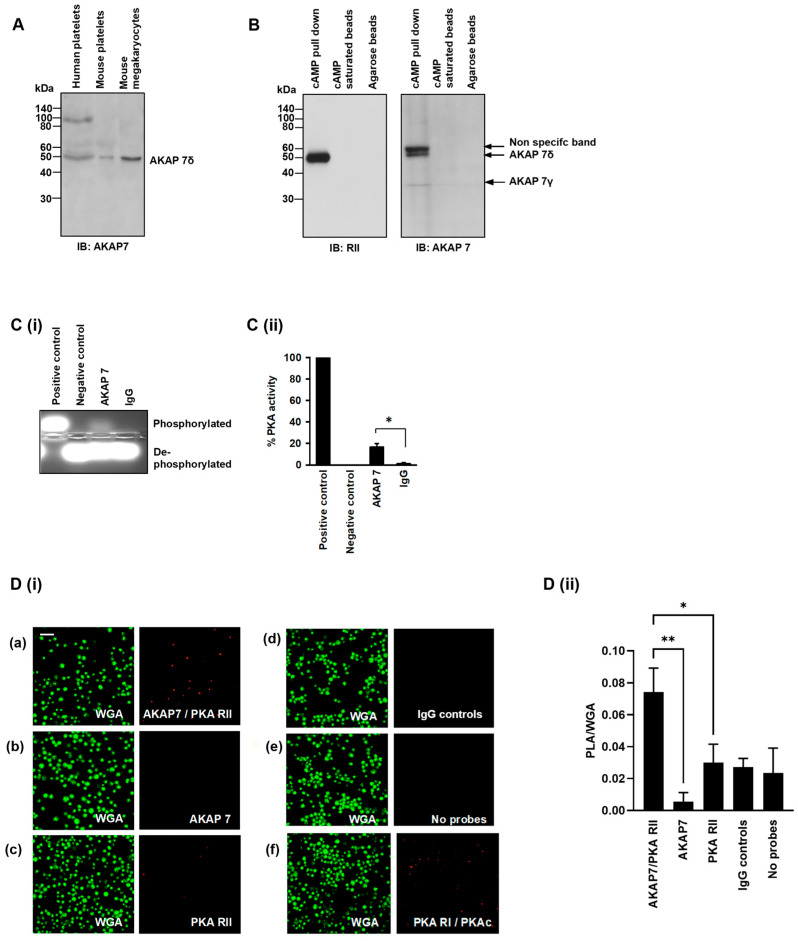
Figure 4.
AKAP7 is expressed and acts as an AKAP in human platelets. (A) Washed human platelet, mouse platelet, and mouse megakaryocytes lysates (20 µg) were immunoblotted for AKAP7 expression. Representative of 3 independent experiments. (B) Washed platelet lysates (1 mg protein) were incubated with cAMP-bound agarose beads ± cAMP (25 µL). Following incubation, the resin, precipitated antigen, and co-immunoprecipitated proteins were isolated by centrifugation and immunoblotted for PKA RII or AKAP7 binding. Representative immunoblots from 3 independent experiments. (C) Washed platelet lysates (500 μg) were incubated with AKAP7 antibody (2 μg) coupled to protein G beads. AKAP7 immunoprecipitates were isolated using centrifugation and analysed for the ability to phosphorylate the synthetic PKA substrate kemptide as a measure of associated PKA. (C(i)) Representative agarose gel image and (C(ii)) Quantification of PKA activity expressed as percentage of PKA activity compared with IgG. Data representative of 3 independent experiments * p < 0.05. (D) Washed platelets (1 × 107 platelets/mL) were subjected to proximity ligation assay to determine physical proximity of the key proteins. (D(i)) Platelets were co-stained with (a) PKA RII and AKAP7 antibodies, (b) AKAP7 alone, (c) PKA RII alone, (d) matched IgG controls, (e) no probes added, and (f) PKA RI and PKAc antibodies as a positive control. Platelet membranes were visualised using wheat germ agglutinin conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488 using fluorescence microscopy. Representative of 4 independent experiments. Scale bar: 10 µm. (D(ii)) Quantification of PLA of 4 independent experiments * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01.