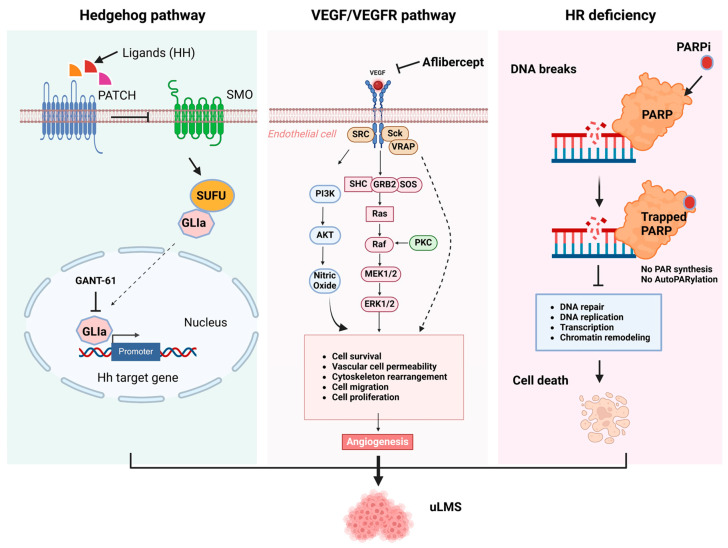
Figure 2.
Abnormal signaling pathways contribute to the pathogenesis of uLMS. Hedgehog pathway (left panel): The signaling pathway is activated by three hedgehog proteins (Hh): sonic hedgehog (Shh), Indian hedgehog (Ihh), and desert hedgehog (Dhh). Hh binds and inactivates a transmembrane protein PATCH. After the binding of Hh, PATCH is sent into the cell and degraded by the proteasome. The PATCH degradation activates Gli proteins, which translocate into the nucleus and switch on specific gene expressions. uLMS showed activated HH signaling. In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrated that targeting GLI with its inhibitor suppressed the uLMS growth. VEGF/VEGFR (middle panel): VEGF binds to the VEGF receptor and triggers the activation of downstream signaling, causing cell survival, vascular cell permeability, cytoskeleton rearrangement, cell migration, and cell proliferation. Targeting VEGF with aflibercept inhibited the uLMS growth. Homogenous recombination (right panel): HR comprises a series of interrelated pathways that repair DNA breaks and interstrand crosslinks. uLMS harbors frequent somatic homozygous BRCA2 deletion, leading to HR deficiency. PARPi competes with NAD+ at the catalytic domain of PARP to block PARP catalytic activity and the formation of PAR polymers, which suppress the DNA replication, DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, and gene transcription in the presence of BRCA 1/2 mutations, eventually causing cell death.