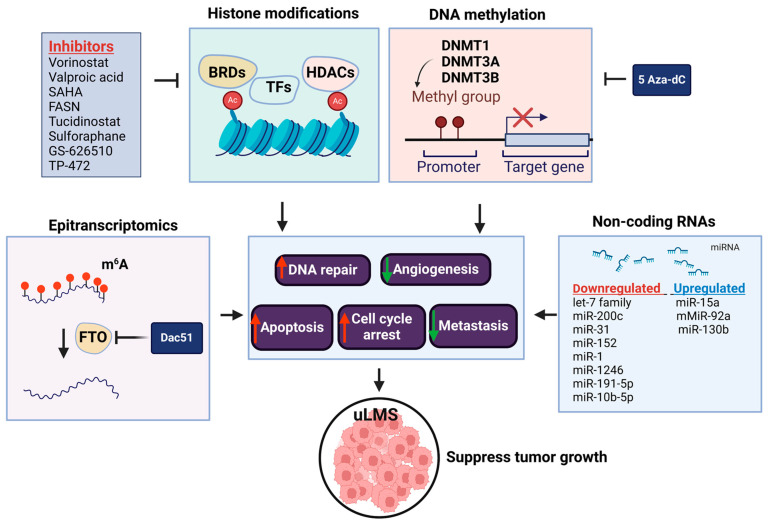
Figure 3.
Abnormal epigenetic/epitranscriptomic regulation contributes to the pathogenesis of uLMS. Histone modification reader BRD9, DNA methyltransferases, class I HDACs, and m6A eraser (FTO) are upregulated in uLMS compared to MM. The targeted inhibition of BRD9, HDACs, and FTO with their small specific inhibitors can inhibit the LMS growth in vitro via induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Red arrows indicate the increased activity of cellular events; Green arrows indicate the decreased activity of biological events.