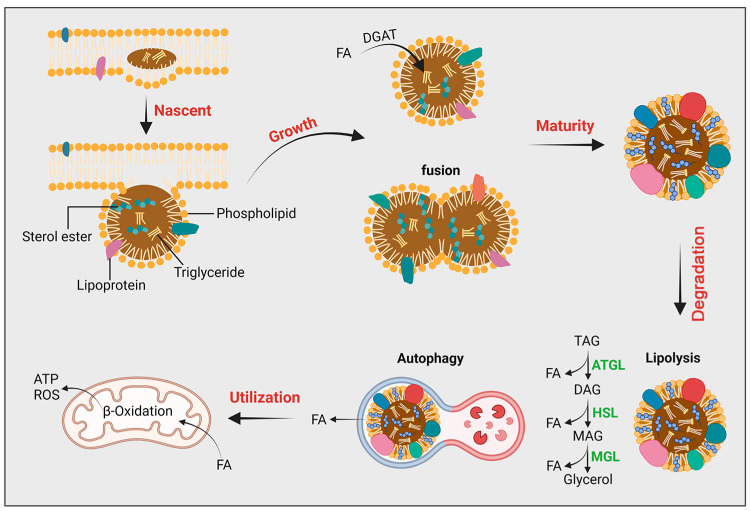
Figure 1.
Composition and metabolic process of lipid droplets: LDs are unique cellular organelles composed of a monolayer of phospholipids surrounding a core of neutral lipids (triglycerides, cholesterol, sterols). They originate from the endoplasmic reticulum, initially accumulating as lens-like structures in the ER membrane and ultimately released into the cytoplasm via budding. Free LDs grow through fusion or autonomous growth, leading to the formation of mature LDs. The surface of LDs contains lipolytic enzymes, activated during starvation, which hydrolyze neutral lipids into fatty acids. Additionally, LDs can be targeted and broken down by autophagolysosomes, releasing fatty acids that undergo beta-oxidation in mitochondria to provide energy. TAG: Triacylglycerol; DAG: Diacylglycerol; MAG: Monoacylglycerol; ATGL: Adipose triglyceride lipase; HSL: Hormone-sensitive lipase; MGL: Monoacylglycerol lipase.