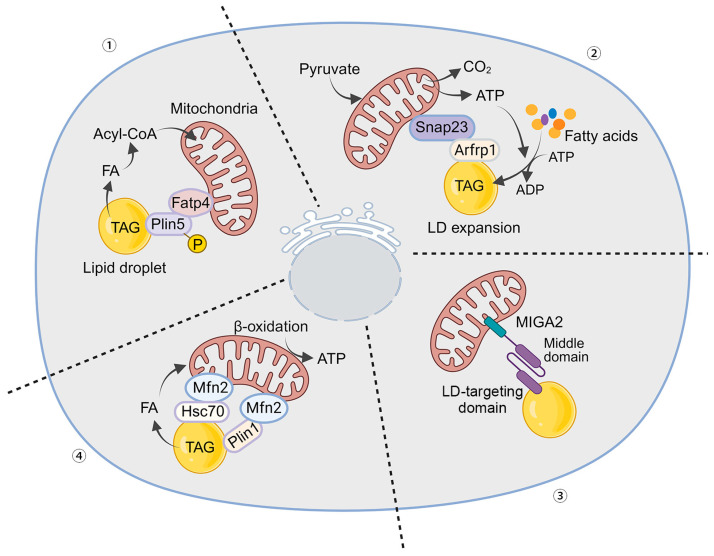
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of Mitochondria–LD Interaction. (1) PLIN5 and FATP4 interaction: The C-terminal structural domain of PLIN5 interacts with FATP4, enhancing the connections between LDs and mitochondria. Starvation triggers the phosphorylation of PLIN5, leading to lipolysis and the release of fatty acids from LDs into mitochondria. These fatty acids are then converted to fatty acyl-CoAs for oxidation. (2) ARFRP1 and SNAP23 recruitment: ARFRP1 recruits SNAP23 to a site near the LD, promoting LD–mitochondria interactions and facilitating LD amplification. (3) MIGA2 linkage: The mitochondrial outer membrane protein MIGA2 links mitochondria to LD proteins, enabling efficient lipid storage within the LD. (4) Mfn2 and Hsc70/PLIN1 complex formation: Mitochondria-localized Mfn2 and LD-localized Hsc70 or PLIN1 form a complex at the mitochondria–LD membrane contact site. This complex tethers mitochondria to the LD, facilitating the transfer of fatty acids from LDs to mitochondria for β-oxidation.