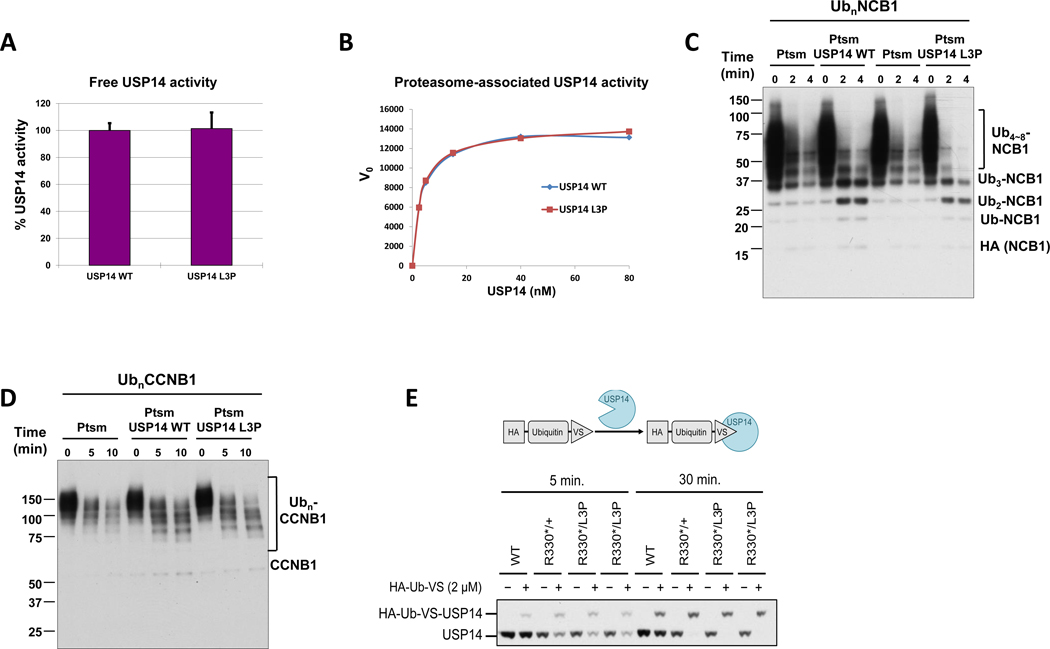
Figure 3. Deubiquitinating activity of recombinant USP14-L3P.
A. Ub-AMC hydrolysis assays with free forms of USP14 WT and L3P at 1.5 μM. Error bars represent S.D. from triplicate experiments. B. Kinetic analysis of proteasome-bound USP14 WT and L3P activities with Ub-AMC as substrate. Graded concentrations of recombinant USP14 were reconstituted with 1 nM Ub-VS-treated proteasome, and cleavage of Ub-AMC (1 μM) by USP14 was measured over 80 min in real time. The plots shown represent mean values of initial reaction rates from triplicate experiments. C. In vitro deubiquitination/degradation assays with UbnNCB1, human proteasome (4 nM), and WT or L3P USP14 (80 nM). D. In vitro deubiquitination/degradation assays with UbnCCNB1, human proteasome (7 nM), and WT or L3P USP14 (140 nM). E. The irreversible covalent modifier ubiquitin vinyl sulfone, carrying an HA epitope tag, was added at 2 micromolar to lysates from patient fibroblasts, and the samples incubated at 25°C for either 5 or 30 min as indicated. Samples were then analyzed by SDS-PAGE and immunoblotting, using an antibody to USP14. Each lane was loaded with 25 micrograms of lysate. HA-Ub-VS reacts with the catalytic cysteine of proteasome-activated USP14.