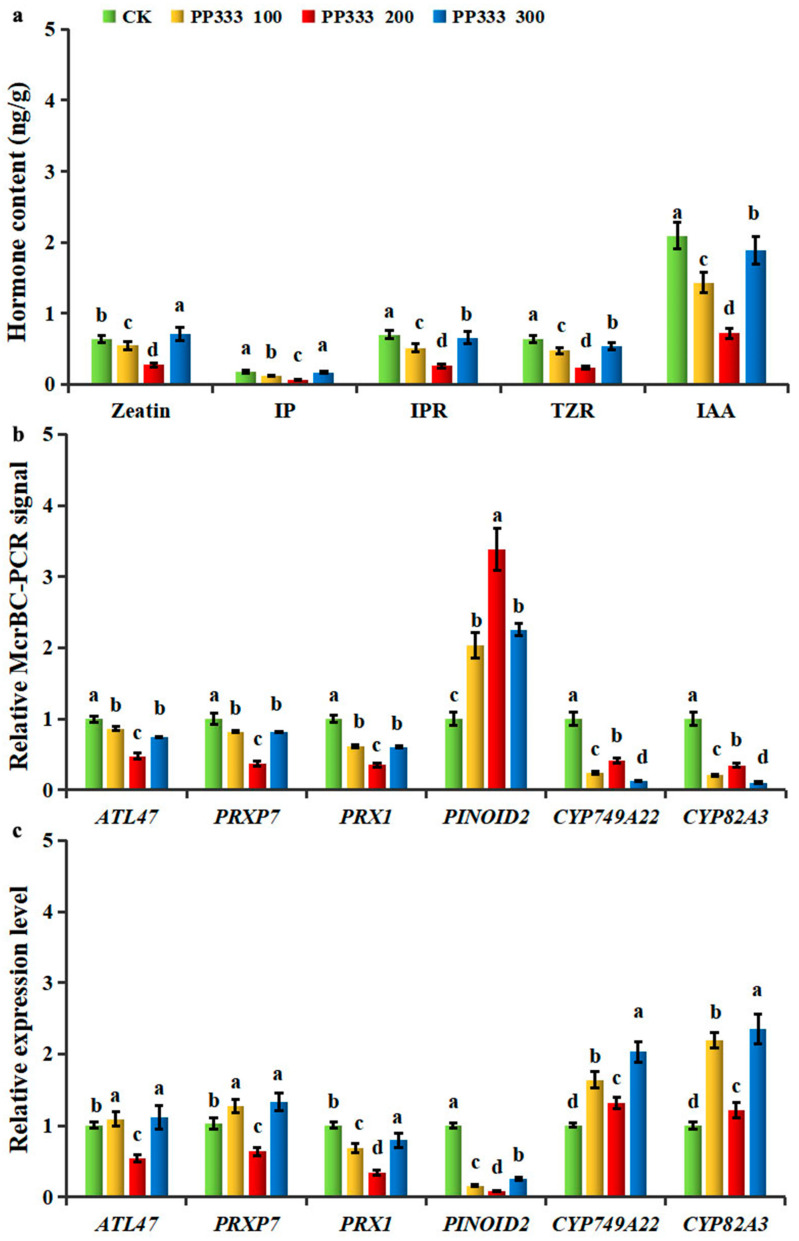
Figure 7.
Exogenous paclobutrazol (PP333) treatment affected gene expression, methylation level, and hormone concentration of pear flower buds. (a) Relative endonuclease McrBC−PCR signal of differentially expressed genes associated with differentially methylated regions (DMEGs) involved in the synthesis, transport, signal transduction, and catabolism pathways of cytokinins and auxin after spraying with different concentrations of PP333. (b) Real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) validation of relative expression levels of the genes after applying different concentrations of paclobutrazol (PP333). (c) Cytokinin and auxin concentrations after applying different concentrations of PP333. CK, PP333 100, PP333 200, and PP333 300 represent four treatment groups which were sprayed with 1000 mLof 0, 100, 200, 300 mg·L−1 paclobutrazol (PP333) in water every 15 days, respectively. Gene IDs: ATL47 (GWHGAAYT013967), PRXP7 (GWHGAAYT055935), PRX1 (GWHGAAYT039634), PINOID2 (GWHGAAYT021140), CYP749A22 (GWHGAAYT046270) and CYP82A3 (GWHGAAYT019719). Hormone abbreviations: IP, N6-isopentenyladenine; IPR, N6-isopentenyladenosine; TZR, trans−zeatin riboside; IAA, indole-3-acetic acid. Vertical bars represent standard deviations (SDs) of the mean of at least three biological replicates. Data (a–c) are presented as the means ± SDs. Values with different lowercase letters are considered significantly different between normal (CKM) and wizened (SM) flower buds (p < 0.05, a one-way ANOVA analysis of variance followed by Duncan’s multiple range test using SPSS26).