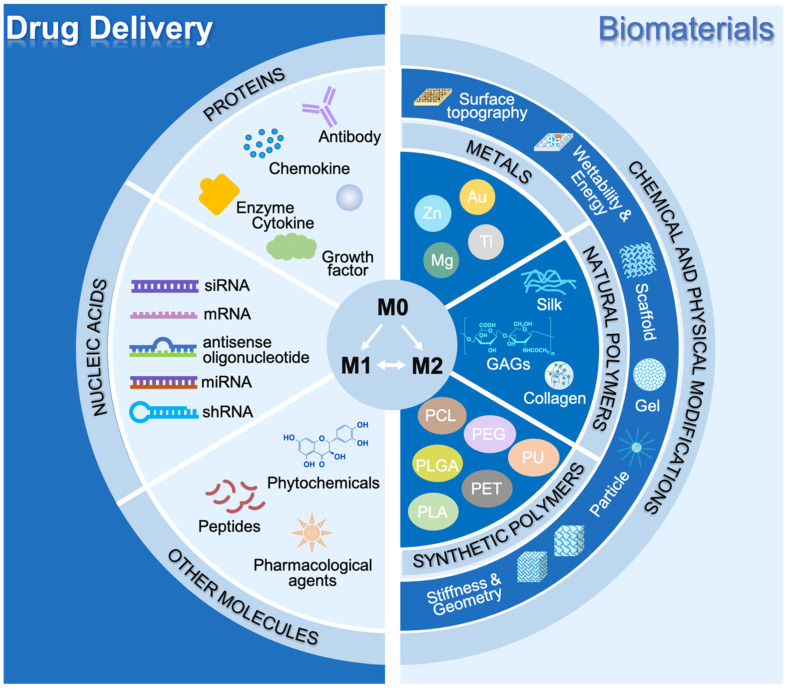
Figure 4.
Therapeutic strategies for modulating macrophage polarization. (1) Drug delivery: immune-instructive modulators, including proteins (such as cytokines, chemokines, antibodies, growth factors, and enzymes), nucleic acids, as well as other anti-inflammatory and/or pro-wound-healing molecules are delivered to damaged tissue, aiming to intervene at different pathway points for the reprogramming of macrophages polarization [173]; (2) Biomaterials: Biomaterials, including metallic materials, natural polymers and synthetic polymers are applied to regulate macrophage polarization to affect the biological behavior of immune factors, while their chemical and physical properties can also affect macrophage phenotypes [30,215,217]. Abbreviations: GAGs, glycosaminoglycans; miRNA, microRNA; mRNA, messenger RNA; PCL, polycaprolactone; PEG, polyethylene glycol; PET, polyethene terephthalate; PLA, polylactic acid; PLGA, poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid); PU, polyurethane; shRNA, small hairpin RNA; siRNA, small interfering RNA.