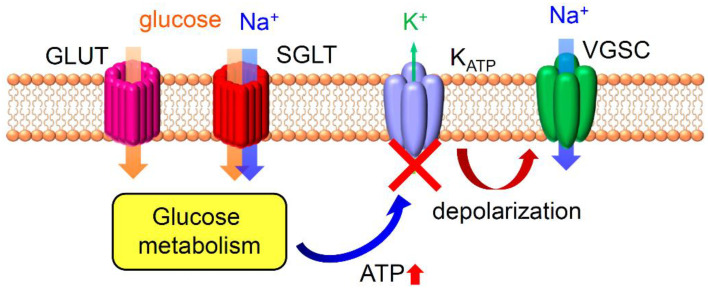
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram showing molecular mechanisms for sweet detection via glucose transporters in taste cells. Glucose entering via glucose transporters (GLUTs) and/or sodium–glucose transporters (SGLTs) is metabolized to produce ATP. The activity of KATP channels is inhibited (indicated by X) by an increase in [ATP]i (indicated by red up arrow), leading to cell depolarization. Na+ entry through SGLTs also induces cell depolarization. Such depolarization activates voltage-gated channels such as voltage-gated sodium channels (VGSCs).