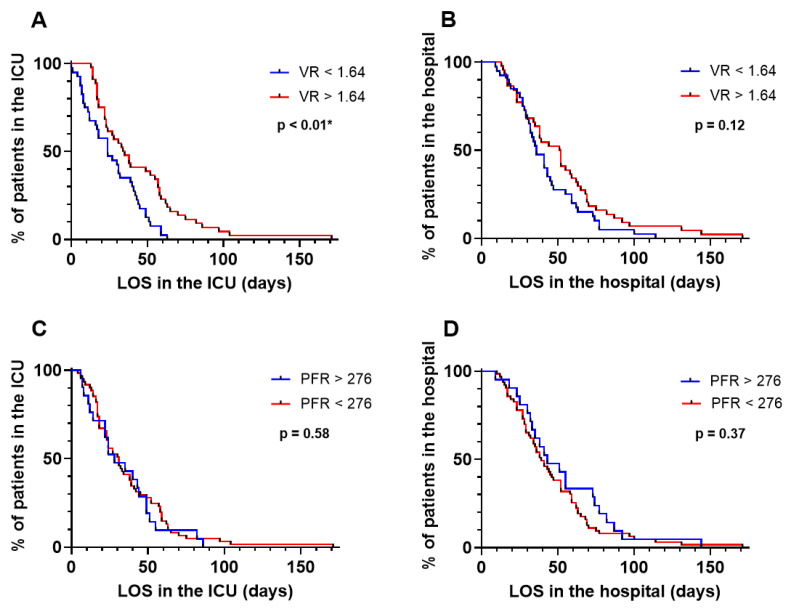
Figure 4.
LOS in the ICU and in the hospital for patients with a VR > 1.64 and a VR < 1.64 and with a PFR > 276 and a PFR < 276. (A) LOS in the ICU of patients with a VR > 1.64 and a VR < 1.64. (B) LOS in the hospital of patients with a VR > 1.64 and a VR < 1.64. Patients with a VR > 1.64 were 2.2 times more likely to have an extended LOS in the ICU compared to those who had a VR < 1.64. There was no significant association between a VR > 1.64 and the LOS in the hospital. LOS: length of stay; ICU: intensive care unit; VR: ventilatory ratio. (C) LOS in the ICU of patients with a PFR > 276 and a PFR < 276. (D) LOS in the hospital of patients with a PFR > 276 and a PFR < 276. There was no significant association between the PFR and LOS in the ICU or hospital. LOS: length of stay; ICU: intensive care unit; PFR: P/F ratio (PaO2/FiO2). Significant results are marked with an *.