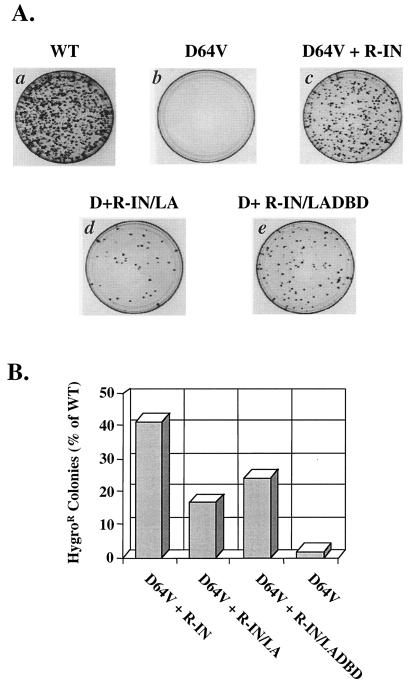
FIG. 3.
The integrase-LexA and integrase-LexA DBD fusion proteins are able to restore integration activity to an HXB-IND64V viral clone. (A) Representative plates of HeLa-CD4 cells infected with 50-ng p24 equivalent of the indicated virus in the hygromycin resistance assay. One million cells were infected for 4 h with viruses carrying the IND64V mutation and containing either R-IN (c), R-IN/LA (d), or R-IN/LADBD (e) fusion proteins. Viruses carrying a wild-type integrase gene served as a positive control (a), and viruses mutated at the D64 residue of integrase were used as a negative control (b). Dark spots on each plate are colonies that grew after selection with medium plus 200 μg of hygromycin B per ml for 12 days, beginning 2 days postinfection. The colonies are a result of provirus formation and stable expression of the hygromycin resistance gene. (B) Relative integration levels of the HXB-IND64V virus complemented with the R-IN/LA and R-IN/LADBD proteins. The data are the average for three independent experiments, each performed with 50-, 5-, and 0.5-ng p24 equivalents of virus in the hygromycin resistance assay. The average number of colonies counted on plates of cells infected with 50-ng p24 equivalent of the wild-type control virus was approximately 1,650.