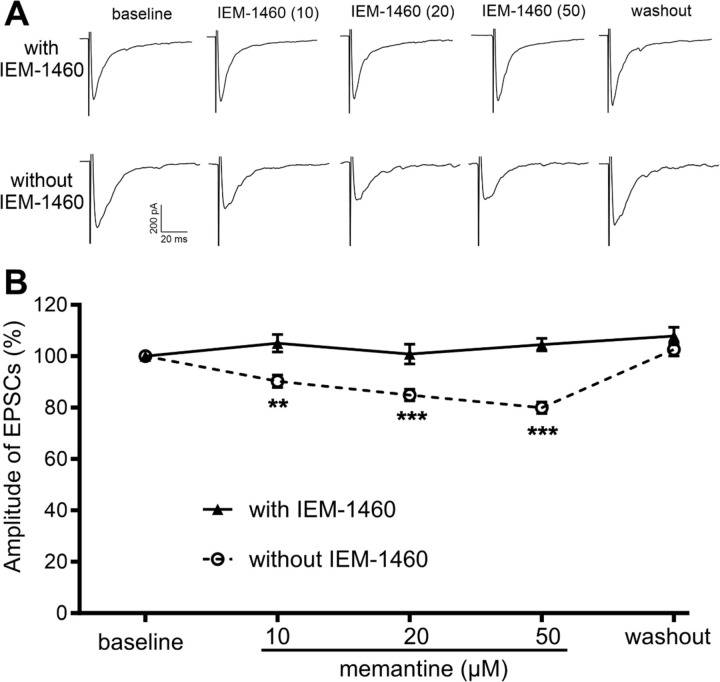
Figure 5. Memantine inhibits synaptic CP-AMPARs in spinal excitatory neurons caused by nerve injury.
A and B, Representative recording traces (A) and quantification (B) illustrate the differential effect of bath application of memantine (10, 20, and 50 µM) on monosynaptically evoked AMPAR-EPSCs in spinal VGluT2 neurons of SNI mice recorded with IEM-1460 (n = 17 neurons from 8 mice) and without IEM-1460 (n = 16 neurons from 8 mice). The data were normalized to the baseline value (100%) immediately prior to memantine application. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, vs. the baseline control within the group (repeated measures ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test).