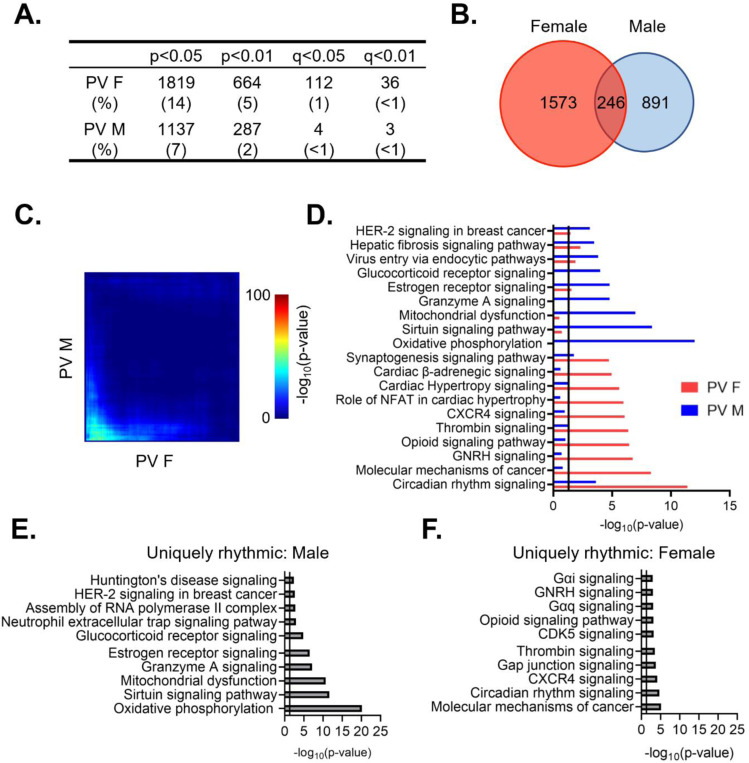
Figure 4. Rhythmic transcripts from PV cells are largely distinct between sexes.
(A) The number of rhythmic transcripts in PV cells isolated from male and female animals at different cutoffs. Females have more rhythmic transcripts at all significance cutoffs. (B) Venn diagram showing the overlap of rhythmic transcripts (p<0.05) between males and females. Few transcripts are rhythmic in both males and females. (C) Threshold-free approach (rank-rank hypergeometric overlap) assessing the overlap of rhythmic transcripts (regardless of p-value) between males and females. Very little overlap confirms that rhythmic transcripts are largely distinct in males and females. (D) The top 10 enriched rhythmic pathways in males and females as determined by Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (Qiagen). Pathways associated with rhythmic transcripts are largely different between males and females. (E)&(F) The top 10 pathways enriched for transcripts that are uniquely rhythmic in either males (E) or females (F), showing sex specific roles of rhythms in PV cells. PV=parvalbumin cells