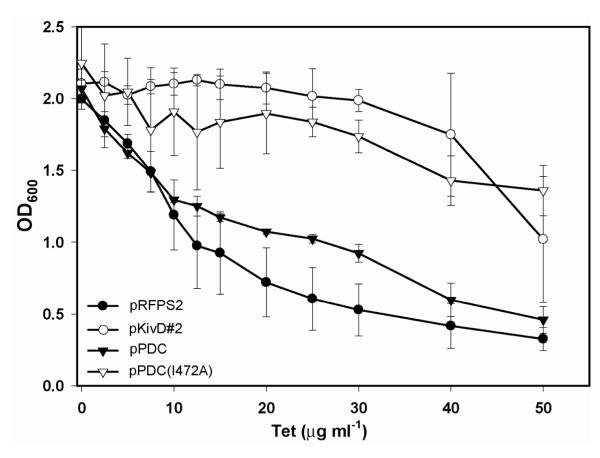
Figure 6. Demonstration of a synthetic selection for in vivo 1-butanol biosynthesis.
E. coli JAD#2 co-transformed with the pSelect#2, TetA-based synthetic selection device and either an RFP control plasmid (pRFPS2) or a non-functional alcohol biosynthetic pathway with a Z. mobilis pyruvate decarboxylase (pPDC) displayed poor growth upon addition of tetracycline selective pressure. Use of the L. lactis promiscuous 2-keto acid decarboxylase pathway (pKivD#2) or introduction of a single point mutation into the Z. mobilis pyruvate decarboxylase (pPDCI472A), imparting 2-oxobutanoate decarboxylase activity, resulted in improved fitness relative to the negative control strains. Data are mean (s.d.) (n=3).